Zeb1-controlled metabolic plasticity enables remodeling of chromatin accessibility in the development of neuroendocrine prostate cancer
- PMID: 38654072
- PMCID: PMC11164927
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-024-01295-5
Zeb1-controlled metabolic plasticity enables remodeling of chromatin accessibility in the development of neuroendocrine prostate cancer
Abstract
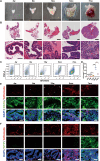
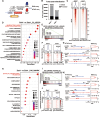
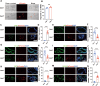
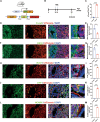
Cell plasticity has been found to play a critical role in tumor progression and therapy resistance. However, our understanding of the characteristics and markers of plastic cellular states during cancer cell lineage transition remains limited. In this study, multi-omics analyses show that prostate cancer cells undergo an intermediate state marked by Zeb1 expression with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), stemness, and neuroendocrine features during the development of neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC). Organoid-formation assays and in vivo lineage tracing experiments demonstrate that Zeb1+ epithelioid cells are putative cells of origin for NEPC. Mechanistically, Zeb1 transcriptionally regulates the expression of several key glycolytic enzymes, thereby predisposing tumor cells to utilize glycolysis for energy metabolism. During this process, lactate accumulation-mediated histone lactylation enhances chromatin accessibility and cellular plasticity including induction of neuro-gene expression, which promotes NEPC development. Collectively, Zeb1-driven metabolic rewiring enables the epigenetic reprogramming of prostate cancer cells to license the adeno-to-neuroendocrine lineage transition.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to ADMC Associazione Differenziamento e Morte Cellulare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zou M, Toivanen R, Mitrofanova A, Floch N, Hayati S, Sun Y, et al. Transdifferentiation as a mechanism of treatment resistance in a mouse model of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:736–49. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1174. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U23A20454/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- NSFC32022021/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- NSFC82372873/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- NSFC81872406/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

