Analysis of the mediating effect between ehealth literacy and health self-management of undergraduate nursing students' mental health literacy
- PMID: 38654311
- PMCID: PMC11036711
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-01920-1
Analysis of the mediating effect between ehealth literacy and health self-management of undergraduate nursing students' mental health literacy
Abstract
Background: Good health self-management positively affects the health of healthcare providers and their ability to manage their patients' health. This study explored the relationship between ehealth literacy, health self-management skills, and mental health literacy among undergraduate nursing students. Some studies have confirmed the correlation between e-health literacy and health self-management skills, while mental health literacy may be correlated with both, and this study aims to explore the relationship between the three.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional survey was conducted at a medical university in northwestern China among 385 Chinese undergraduate nursing students. Participants completed the General Information Questionnaire, the Adult Health Self-Management Skills Rating Scale, the Mental Health Literacy Rating Scale, and the eHealth Literacy Scale, and provided valid responses. The IBM SPSS 27.0 statistical software was used for data entry and descriptive analysis, t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson correlation analysis. The IBM Amos 26.0 was used to construct the mediation effect model, and the Bootstrap method was employed to test mediating effects.
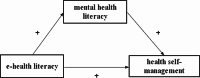
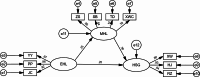
Results: Mental health literacy, ehealth literacy, and health self-management skills of undergraduate nursing students were at a moderate to high level. Mental health literacy, ehealth literacy, and health self-management were positively correlated. Mental health literacy, particularly, played a partial mediating role of 31.1% ( 95% CI [0.307-1.418] ) between ehealth literacy and health self-management.
Conclusions: Undergraduate nursing students' mental health literacy partially mediates the link between eHealth literacy and health self-management skills. Schools should emphasize the development of nursing students' e-health literacy and mental health literacy in order to improve their health self-management skills, which will not only bring about a better health outcome for the students, but will also benefit the health of the social population.
Keywords: Anxiety; Health literacy; Mental health; Nursing education; Nursing students; Questionnaire design; Self-management.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perceived eHealth Literacy and Learning Experiences Among Japanese Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Cross-sectional Study.Comput Inform Nurs. 2020 Apr;38(4):198-203. doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000000611. Comput Inform Nurs. 2020. PMID: 31990809
-
The relationship between eHealth literacy, social media self-efficacy and health communication intention among Chinese nursing undergraduates: A cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 31;10:1030887. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1030887. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36388375 Free PMC article.
-
eHealth literacy among undergraduate nursing students.Nurse Educ Today. 2016 Jul;42:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nurse Educ Today. 2016. PMID: 27237352
-
COVID-19 crisis: Influence of eHealth literacy on mental health promotion among Saudi nursing students.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021 Dec;16(6):906-913. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2021.07.008. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34803568 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic health-literacy skills among nursing students.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2019 Jul 18;10:527-532. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S207353. eCollection 2019. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2019. PMID: 31410077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Health Self-Management Behaviors as a Bridge Between Electronic Health Literacy and Health-Related Quality of Life: Cross-Sectional Study From China.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Aug 13;27:e74056. doi: 10.2196/74056. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40802975 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating digital and interactive approaches in adolescent health literacy: a comprehensive review.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 9;12:1387874. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1387874. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39444982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of information anxiety on core competency of registered nurses: mediating effect of digital health literacy.BMC Nurs. 2024 Sep 6;23(1):626. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02275-3. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39243073 Free PMC article.
-
eHealth Literacy and Its Outcomes Among Postsecondary Students: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jul 2;27:e64489. doi: 10.2196/64489. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40601925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital health literacy among undergraduate nursing students in China: associations with health lifestyles and psychological resilience.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Oct 14;24(1):1139. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06075-w. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39402500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Constitution of the world health organization. 1946. https://www.who.int/fr/about/governance/constitution. Accessed 27 May 2023.
-
- Liu W, lv B. Health and longevity and self-care. Anhui Clin J Chin Med. 2002;14:218.
-
- Corbin JM, Strauss A. Unending work and care: managing chronic illness at Home. Contemp Sociol. 1989;18:945. doi: 10.2307/2074227. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources