The association between the degree of cervical dilatation before ultrasound and physical examination indicated cerclage and subsequent neonatal outcomes
- PMID: 38654815
- PMCID: PMC11037092
- DOI: 10.5339/qmj.2024.20
The association between the degree of cervical dilatation before ultrasound and physical examination indicated cerclage and subsequent neonatal outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: Preterm identification of cervical dilation in pregnant women leads to the application of emergency cervical cerclage with an expectation of achieving term delivery. However, this is not always feasible. Short- and long-term neonatal complications post-preterm birth pose a significant challenge. It is crucial to anticipate potential complications and understand the possibilities of postpartum development as they can be encountered. We aimed to evaluate the effect of the degree of cervical dilatation before ultrasound and physical examination-indicated cerclage in singleton pregnancies presenting with premature cervical dilatation with bulging fetal membranes (rescue cerclage) on subsequent neonatal outcomes.
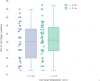
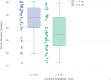
Materials and methods: In this retrospective clinical study, over a 10-year period between January 2009 and January 2019, 72 singleton pregnancies undergoing rescue cerclage were included and divided into two groups according to pre-cerclage cervical dilatation: Group 1 (n = 33) and Group 2 (n = 39) with cervical dilatation ≤3 cm and >3 cm, respectively. Latency period for pregnancy prolongation, gestational age at delivery, birth weight, and neonatal morbidity and mortality were compared across the groups. Logistic regression was used to delineate the independent effect of cervical dilatation at cerclage placement on neonatal mortality.
Results: Group 2 had a higher delivery rate at ≤28 weeks' gestation (p = 0.007) and lower birth weight (p = 0.002) compared to Group 1, with an increased mean latency period in Group 2 (90 ± 55 days versus 52 ± 54 days, p = 0.005). The newborn intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), neonatal jaundice and sepsis, and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) were more frequent in Group 2. Neonatal mortality rate was higher (52.6% versus 24.2%, p = 0.015) and intact survival was lower (23.1% versus 48.4%, p = 0.013) in Group 2, whereas rates of cerebral palsy (8% and 9%, respectively) were similar between the groups (p = 0.64).
Conclusion: Advanced cervical dilatation (>3 cm) during physical examination-indicated cerclage in singleton pregnancies is associated with earlier delivery, leading to increased neonatal morbidity and mortality when compared with pregnancies having lesser degrees of cervical dilatation at cerclage. However, short-term poor neurological outcomes seem comparable.
Keywords: McDonald cerclage; cervical dilatation; emergency cerclage; neonatal outcomes; preterm delivery.
© 2024 Turgut, Erdemoğlu, Dağdelen, Gürdal, Özkaya, Sezik, Licensee HBKU Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ozgur Akkurt M, Yavuz A, Sezik M, Okan Ozkaya M. Infant outcomes following midtrimester emergency cerclage in the presence of fully dilated cervix and prolapsing amniotic membranes into the vagina. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;;29((15):):2438-42. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2015.1087495. doi: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources