Factors influencing self-care management in adult hemodialysis patients: An integrative review
- PMID: 38654818
- PMCID: PMC11037095
- DOI: 10.5339/qmj.2024.12
Factors influencing self-care management in adult hemodialysis patients: An integrative review
Abstract
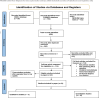
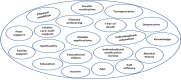
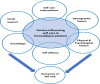
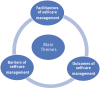
Background: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) poses a significant health challenge, with hemodialysis (HD) being the most prevalent therapy. Patients undergoing HD must comply with a strict therapeutic regimen, including dietary control, fluid restriction, and medication adherence. Successful disease management and improved outcomes rely on patients' involvement and participation in their care. Aim: To identify the factors that hinder or facilitate self-care management (SCM) in HD patients. Methodology: This review followed Whittemore and Knafl's integrative review framework. A comprehensive literature search of articles published between 2017 and 2022 was conducted in CINAHL, Medline, and PubMed using the keywords end-stage renal disease, hemodialysis, self-care management, self-care, and self-management. This search yielded 21 suitable articles for review. Results: SCM is influenced by three main factors: facilitators, barriers, and outcomes. Facilitators of SCM include self-care management interventions, patient knowledge, socio-demographic factors, family support, healthcare professionals, peer support, and psychological factors. Barriers encompass psychological and physical conditions. Outcomes include both physiological and psychological aspects. Conclusion: Understanding the factors influencing SCM in HD patients is vital for developing reliable and effective self-care strategies and interventions to enhance both physical and psychological outcomes.
Keywords: barriers; end-stage renal disease; facilitators; hemodialysis; self-care management.
© 2024 Yasin, Khraim, Santos, Forgrave, Hamad, Licensee HBKU Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
Treatment Adherence and Factors Influencing It in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Study From a Tertiary Care Hospital in North India.Cureus. 2024 Nov 9;16(11):e73335. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73335. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39655099 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of the Qualitative Research on Barriers and Facilitators to Home Hemodialysis.Hemodial Int. 2025 May 26. doi: 10.1111/hdi.13266. Online ahead of print. Hemodial Int. 2025. PMID: 40417777 Review.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric pain management: knowledge, attitudes, barriers and facilitators among nurses - integrative review.Int Nurs Rev. 2018 Dec;65(4):524-533. doi: 10.1111/inr.12465. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Int Nurs Rev. 2018. PMID: 29956310
Cited by
-
Predictors of self-management behaviors among patients undergoing hemodialysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 22;15(1):13823. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97414-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40263506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Malki H, Rashed AH, Asim M. Renal replacement therapy in Qatar—past, present and future. Open Journal of Nephrology. 2018 Jun 14;;8((02):):42.
-
- Hemodialysis [Internet] 2021 [cited 2021 Jul 29] Available from: https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/hemodialysis.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources