Temporal Changes in the Local Expression of Central Hormone-Regulating Factors in Rat Testis
- PMID: 38654975
- PMCID: PMC11034993
- DOI: 10.12717/DR.2024.28.1.21
Temporal Changes in the Local Expression of Central Hormone-Regulating Factors in Rat Testis
Abstract
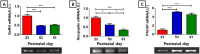
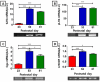
Present study aimed to investigate the temporal changes in expression of some reproductive hormones in testis, originally found in hypothalamus and pituitary. Rats were sacrificed on postnatal day 23 (PND23; immature), pubertal (PND53) and PND 81 (young adult). The testicular RNAs were extracted, and semi-quantitative PCRs for gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), kisspeptin 1 (KiSS1), pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP), LH subunits and LH receptor were performed. Transcript levels of GnRH and KiSS1 at PND23 were significantly higher than levels of PND53 and PND81 (p<0.001). PACAP mRNA level at PND23 was significantly lower than those of PND53 and PND81 (p<0.001). The mRNA levels of both testis type and pituitary type luteinizing hormone β subunit (tLHβ and pLHβ, respectively) at PND23 were significantly lower than levels of PND53 and PND81 (p<0.001). The mRNA level of glycoprotein hormone common alpha subunit (Cgα) at PND23 was significantly lower than those of PND53 and PND81 (p<0.001). Present study revealed the intratesticular expression of KiSS1 and GnRH showed a very similar trend while the expression of PACAP in the testis showed reversed pattern. The expressions of LHβ subunits (tLHβ and pLHβ) were very low during immature stage then increased significantly during puberty and early adulthood. Our attempt to study the local role(s) of intratesticular factors will be helpful to achieve precise understanding on the testis physiology and pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anjum S, Krishna A, Sridaran R, Tsutsui K. Localization of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH), kisspeptin and GnRH receptor and their possible roles in testicular activities from birth to senescence in mice. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2012;317:630–644. doi: 10.1002/jez.1765. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahk JY, Hyun JS, Chung SH, Lee H, Kim MO, Lee BH, Choi WS. Stage specific identification of the expression of GnRH mRNA and localization of the GnRH receptor in mature rat and adult human testis. J Urol. 1995;154:1958–1961. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66834-4. doi: 10.1097/00005392-199511000-00105. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi WS, Lee SH, Cho BN, Baik SH, Yoon YD, Lee CC, Kim K. Expression and cellular localization of gonadotropin releasing hormone in the rat gonad. Mol Cells. 1994;4:267–272. doi: 10.1016/S1016-8478(23)17235-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

