Molecular targeted therapies for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and clinical implications
- PMID: 38655092
- PMCID: PMC11036065
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2023-6489
Molecular targeted therapies for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and clinical implications
Abstract
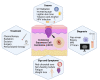
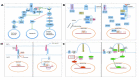
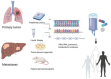
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) is a common and potentially fatal type of skin cancer that poses a significant threat to public health and has a high prevalence rate. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin surface increases the risk of cSCC, especially in those with genetic syndromes like xerodermapigmentosum and epidermolysis bullosa. Therefore, understanding the molecular pathogenesis of cSCC is critical for developing personalized treatment approaches that are effective in cSCC. This article provides a comprehensive overview of current knowledge of cSCC pathogenesis, emphasizing dysregulated signaling pathways and the significance of molecular profiling. Several limitations and challenges associated with conventional therapies, however, are identified, stressing the need for novel therapeutic strategies. The article further discusses molecular targets and therapeutic approaches, i.e., epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, hedgehog pathway inhibitors, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors, as well as emerging molecular targets and therapeutic agents. The manuscript explores resistance mechanisms to molecularly targeted therapies and proposes methods to overcome them, including combination strategies, rational design, and optimization. The clinical implications and patient outcomes of molecular-targeted treatments are assessed, including response rates and survival outcomes. The management of adverse events and toxicities in molecular-targeted therapies is crucial and requires careful monitoring and control. The paper further discusses future directions for therapeutic advancement and research in this area, as well as the difficulties and constraints associated with conventional therapies.
Keywords: clinical implications; clinical trials; combination strategies; patient; skin cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular genetics of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: perspective for treatment strategies.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May;34(5):932-941. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16098. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 31747091 Review.
-
Current Advances and Challenges in the Management of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Immunosuppressed Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;16(18):3118. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183118. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC): Challenges and emerging therapies.Asian J Surg. 2023 Jan;46(1):47-51. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.04.079. Epub 2022 May 8. Asian J Surg. 2023. PMID: 35545474 Review.
-
Growth and Viability of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Display Different Sensitivities to Isoform-Specific Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3567. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073567. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808215 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous adverse effects of targeted therapies: Part II: Inhibitors of intracellular molecular signaling pathways.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 Feb;72(2):221-36; quiz 237-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.07.033. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25592339 Review.
Cited by
-
Gold nanostructures in melanoma: Advances in treatment, diagnosis, and theranostic applications.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 2;10(15):e35655. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35655. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnological Advances in the Diagnosis of Gynecological Cancers and Nanotheranostics.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(33):2619-2630. doi: 10.2174/0113816128317605240628063731. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39021196 Review.
-
DEB-TACE combined with ici for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: a case report.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 22;15:1529976. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1529976. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40330832 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-based Liposomal Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery in Lung Cancer Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Outlooks.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(36):2850-2881. doi: 10.2174/0113816128304923240704113319. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39051580 Review.
References
-
- Albahri A, Duhaim AM, Fadhel MA, Alnoor A, Baqer NS, Alzubaidi L, et al. A systematic review of trustworthy and explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare: Assessment of quality, bias risk, and data fusion. Information Fusion. 2023;96:156–191.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
