Impacts of futile reperfusion and reperfusion injury in acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 38655438
- PMCID: PMC11034445
- DOI: 10.4103/bc.bc_9_24
Impacts of futile reperfusion and reperfusion injury in acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
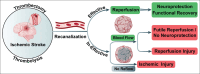
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) remains to be a challenging cerebrovascular disease. The mainstay of AIS management is endovascular reperfusion therapy, including thrombectomy and thrombolysis. However, ineffective (futile) reperfusion (FR) or reperfusion injury (RI) can be seen in a significant number of patients undergoing reperfusion strategy. In this article, we discuss two clinically relevant concepts known as "time window" and "tissue window" that can impact the clinical outcome of reperfusion therapy. We also explore patient risk factors, leading to FR and RI as well as an emerging concept of "no-reflow phenomenon" seen in ineffective reperfusion. These fundamental concepts provide insight into the clinical management of AIS patients and provide references for future research.
Keywords: Endovascular reperfusion therapy; ineffective (futile) reperfusion; no-reflow phenomenon; thrombectomy; thrombolysis; time window; tissue window.
Copyright: © 2024 Brain Circulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Yuchuan Ding is an Associate Editor of Brain Circulation. The article was subject to the journal’s standard procedures, with peer review handled independently of this editor and their research groups.
Figures
References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update:A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–639. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Xiong Y. Advances in futile reperfusion following endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion. Eur Neurol. 2023;86:95–106. - PubMed
-
- Nie X, Leng X, Miao Z, Fisher M, Liu L. Clinically ineffective reperfusion after endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2023;54:873–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
