Regioselective C(sp2)-H halogenation of pyrazolo[1,5- a]pyrimidines facilitated by hypervalent iodine(iii) under aqueous and ambient conditions
- PMID: 38655480
- PMCID: PMC11036372
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra02090a
Regioselective C(sp2)-H halogenation of pyrazolo[1,5- a]pyrimidines facilitated by hypervalent iodine(iii) under aqueous and ambient conditions
Abstract
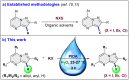
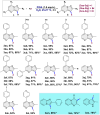
An efficient and mild approach has been developed for the regio-selective direct C3 halogenation of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines employing readily available potassium halide salts and a hypervalent iodine(iii) reagent at ambient temperature. The protocol is both practical and environmentally friendly, utilizing water as a green solvent, potassium halides as an inexpensive and bench stable halogen source and PIDA as a non-toxic reagent, enabling clean and efficient halogenation at room temperature. The procedure yields a range of C3 halogenated pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines in good to excellent yields. Mechanistic studies suggest the involvement of electrophilic substitution mechanism in the halogenation process.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Promoted C3-H Regioselective Halogenation of 4-Quinolones under Mild Conditions.ACS Omega. 2021 Nov 29;6(49):34044-34055. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05455. eCollection 2021 Dec 14. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34926952 Free PMC article.
-
A Green Chemical Approach for Iodination of Pyrimidine Derivatives by Mechanical Grinding under Solvent-Free Conditions.Molecules. 2022 Sep 27;27(19):6386. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196386. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234918 Free PMC article.
-
Regioselective C-H Thio- and Selenocyanation of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines.Chem Asian J. 2025 May 2;20(9):e202401610. doi: 10.1002/asia.202401610. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Chem Asian J. 2025. PMID: 39912247
-
Hypervalent iodine-mediated intramolecular alkene halocyclisation.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2024 Nov 28;20:3113-3133. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.20.258. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2024. PMID: 39624657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophilic halogenation-reductive elimination chemistry of organopalladium and -platinum complexes.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Feb 17;48(2):238-47. doi: 10.1021/ar500325x. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25602260 Review.
References
-
- Fujimori D. G. Walsh C. T. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007;11:553–560. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.08.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Hughes C. C. MacMillan J. B. Gaudêncio S. P. Jensen P. R. Fenical W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009;48:725–727. doi: 10.1002/anie.200804890. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Kaur K. Jain M. Reddy R. P. Jain R. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010;45:3245–3264. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.04.011. - DOI - PubMed
- Vandekerckhove S. Tran H. G. Desmet T. D’hooghe M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013;23:4641–4643. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.06.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gál B. Bucher C. Burns N. Z. Mar. Drugs. 2016;14:206. doi: 10.3390/md14110206. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Quémener M. Kikionis S. Fauchon M. Toueix Y. Aulanier F. Makris A. M. Roussis V. Ioannou E. Hellio C. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:32. doi: 10.3390/md20010032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Wang C. Du W. Lu H. Lan J. Liang K. Cao S. Molecules. 2021;26:2754. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092754. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Winterton N. Green Chem. 2000;2:173–225. doi: 10.1039/B003394O. - DOI
-
- Fairlamb I. J. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007;36:1036–1045. doi: 10.1039/B611177G. - DOI - PubMed
- Hooshmand S. E. Heidari B. Sedghi R. Varma R. S. Green Chem. 2019;21:381–405. doi: 10.1039/C8GC02860E. - DOI
- Kambe N. Iwasaki T. Terao J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:4937–4947. doi: 10.1039/C1CS15129K. - DOI - PubMed
- Ruiz-Castillo P. Buchwald S. L. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:12564–12649. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sun C. L. Li H. Yu D. G. Yu M. Zhou X. Lu X. Y. Huang K. Zheng S. F. Li B. J. Shi Z. J. Nat. Chem. 2010;2:1044–1049. doi: 10.1038/nchem.862. - DOI - PubMed
- Sun C. L. Shi Z. J. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:9219–9280. doi: 10.1021/cr400274j. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dorababu A. Arch. Pharm. 2022;355:2200154. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202200154. - DOI - PubMed
- Johansson N. G. Dreano L. Vidilaseris K. Khattab A. Liu J. Lasbleiz A. Ribeiro O. Kiriazis A. Boije af Gennäs G. Meri S. Goldman A. Yli-Kauhaluoma J. Xhaard H. ChemMedChem. 2021;16:3360–3367. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100392. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Kiessling A. Wiesinger R. Sperl B. Berg T. ChemMedChem. 2007;2:627–630. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200600294. - DOI - PubMed
- McGillan P. Berry N. G. Nixon G. L. Leung S. C. Webborn P. J. H. Wenlock M. C. Kavanagh S. Cassidy A. Clare R. H. Cook D. A. Johnston K. L. Ford L. Ward S. A. Taylor M. J. Hong W. D. O'Neill P. M. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021;12:1421–1426. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00216. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

