Shenkang injection for the treatment of acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38655870
- PMCID: PMC11044765
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2338566
Shenkang injection for the treatment of acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Shenkang injection (SKI) has been widely used in China for many years for the treatment of kidney disease. The objective of this systematic review was to assess the efficacy of Shenkang injection for the treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI).
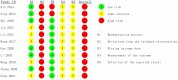
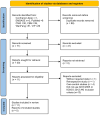
Methods: A search was conducted across seven databases, encompassing data from the inception of each database through October 8th, 2023. Randomized controlled trials comparing SKI-treated AKI patients with control subjects were extracted. The main outcome measure was serum creatinine (SCr) levels. Secondary outcomes included blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum cystatin C (CysC), 24-h urine protein (24 h-Upro) levels, APACHE II score and adverse reactions.
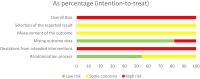
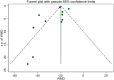
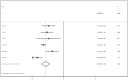
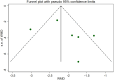
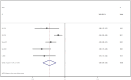
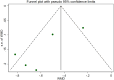
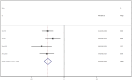
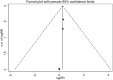
Results: This meta-analysis included eleven studies, and the analysis indicated that, compared with the control group, SKI significantly decreased SCr [WMD = -23.31, 95% CI (-28.06, -18.57); p < 0.001]; BUN [WMD = -2.07, 95% CI (-2.56, -1.57); p < 0.001]; CysC [WMD = -0.55, 95% CI (-0.78, -0.32), p < 0.001]; 24-h urine protein [WMD = -0.43, 95% CI (-0.53, -0.34), p < 0.001]; and the APACHE II score [WMD = -3.07, 95% CI (-3.67, -2.48), p < 0.001]. There was no difference in adverse reactions between the SKI group and the control group [RR = 1.32, 95% CI (0.66, 2.63), p = 0.431].
Conclusion: The use of SKI in AKI patients may reduce SCr, BUN, CysC, 24-h Upro levels, and APACHE II scores in AKI patients. The incidence of adverse reactions did not differ from that in the control group. Additional rigorous clinical trials will be necessary in the future to thoroughly evaluate and establish the effectiveness of SKI in the treatment of AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Shenkang injection; meta-analysis; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures









Similar articles
-
Shenkang injection combined with alprostadil for chronic renal failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 6;10:982016. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.982016. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37089596 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect and underlying mechanism of Shenkang injection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 30;301:115805. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115805. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36216195
-
Shenkang injection improves coagulation in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Aug;39(4):451-458. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186091
-
Association of definition of acute kidney injury by cystatin C rise with biomarkers and clinical outcomes in children undergoing cardiac surgery.JAMA Pediatr. 2015 Jun;169(6):583-91. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.54. JAMA Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25844892 Free PMC article.
-
Furosemide does not reduce the incidence of postoperative acute kidney injury in adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.J Card Surg. 2022 Dec;37(12):4850-4860. doi: 10.1111/jocs.17120. Epub 2022 Nov 8. J Card Surg. 2022. PMID: 36345680
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Shenkang Injection combined with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers in diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2499231. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2499231. Epub 2025 May 27. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40425314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of traditional Chinese medicines in regulating acute kidney injury-related ferroptosis: a literature review.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 May;57(5):1601-1608. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04302-3. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39680293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kidney Disease: improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group . Kdigo clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:1–138. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2012.1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
