Resveratrol mediates mitochondrial function through the sirtuin 3 pathway to improve abnormal metabolic remodeling in atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 38656259
- PMCID: PMC11064893
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4004
Resveratrol mediates mitochondrial function through the sirtuin 3 pathway to improve abnormal metabolic remodeling in atrial fibrillation
Abstract
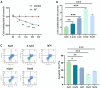
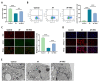
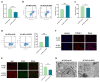
This study investigated the impact of resveratrol on abnormal metabolic remodeling in atrial fibrillation (AF) and explored potential molecular mechanisms. An AF cell model was established by high-frequency electrical stimulation of HL-1 atrial muscle cells. Resveratrol concentrations were optimized using CCK-8 and flow cytometry. AF-induced increases in ROS and mitochondrial calcium, along with decreased adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and mitochondrial membrane potential, were observed. Resveratrol mitigated these changes and maintained normal mitochondrial morphology. Moreover, resveratrol acted through the SIRT3-dependent pathway, as evidenced by its ability to suppress AF-induced acetylation of key metabolic enzymes. SIRT3 overexpression controls acetylation modifications, suggesting its regulatory role. In conclusion, resveratrol's SIRT3-dependent pathway intervenes in AF-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, presenting a potential therapeutic avenue for AF-related metabolic disorders. This study sheds light on the role of resveratrol in mitigating AF-induced mitochondrial remodeling and highlights its potential as a novel treatment for AF.
Figures

References
-
- Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, Cabana M, Caughey AB, Davis EM, et al. Screening for atrial fibrillation: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2022;327:360-7. - PubMed
-
- Rahman F, Kwan GF, Benjamin EJ. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Cardiol 2014;11:639-54. - PubMed
-
- Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F, Cervellin G. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge. Int J Stroke 2021;16:217-21. - PubMed
-
- Wijesurendra RS, Casadei B. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2019;105:1860-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

