Design and synthesis of new quinazolinone derivatives: investigation of antimicrobial and biofilm inhibition effects
- PMID: 38656598
- PMCID: PMC11785708
- DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-10830-y
Design and synthesis of new quinazolinone derivatives: investigation of antimicrobial and biofilm inhibition effects
Abstract
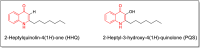
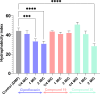
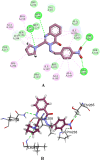
New quinazolin-4-ones 9-32 were synthesized in an attempt to overcome the life-threatening antibiotic resistance phenomenon. The antimicrobial screening revealed that compounds 9, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20 and 29 are the most broad spectrum antimicrobial agents in this study with safe profile on human cell lines. Additionally, compounds 19 and 20 inhibited biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is regulated by quorum sensing system, at sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) with IC50 values 3.55 and 6.86 µM, respectively. By assessing other pseudomonal virulence factors suppression, it was found that compound 20 decreased cell surface hydrophobicity compromising bacterial cells adhesion, while both compounds 19 and 20 curtailed the exopolysaccharide production which constitutes the major component of the matrix binding biofilm components together. Also, at sub-MICs Pseudomonas cells twitching motility was impeded by compounds 19 and 20, a trait which augments the cells pathogenicity and invasion potential. Molecular docking study was performed to further evaluate the binding mode of candidates 19 and 20 as inhibitors of P. aeruginosa quorum sensing transcriptional regulator PqsR. The achieved results demonstrate that both compounds bear promising potential for discovering new anti-biofilm and quorum quenching agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa without triggering resistance mechanisms as the normal bacterial life cycle is not disturbed.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Antimicrobial; Biofilm inhibition; Quinazolinones.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors do not have conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Novel quinazolinone inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing transcriptional regulator PqsR.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 15;208:112778. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112778. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32927392 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3-amino-2-oxazolidinone derivatives as potent quorum-sensing inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 May 15;194:112252. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112252. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32244097
-
Novel quinazolinone disulfide analogues as pqs quorum sensing inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jan;130:106226. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106226. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36332317
-
Anti-PqsR compounds as next-generation antibacterial agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jun 15;172:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.049. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30939351 Review.
-
Critical review on plant-derived quorum sensing signaling inhibitors in pseudomonas aeruginosa.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Oct;151:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107649. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39029321 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial Activity and Antifungal Activity of Monomeric Alkaloids.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 12;16(11):489. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110489. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Quinazolinones Active against Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Synthesis, Antimicrobial Evaluation, and in Silico Exploration of Penicillin-Binding Protein 1A as a Potential Target.ChemMedChem. 2025 Jul 1;20(13):e202500147. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202500147. Epub 2025 Jun 8. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 40237183 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in quinazolinone derivatives: structure, design and therapeutic potential.Future Med Chem. 2025 May;17(9):1071-1091. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2504327. Epub 2025 May 11. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40350383 Review.
References
-
- El-Gohary NS, Shaaban MI (2015) Antimicrobial and antiquorum-sensing studies. Part 3: synthesis and biological evaluation of new series of [1,3,4]thiadiazoles and fused [1,3,4]thiadiazoles. Arch Pharm 348:283–297. 10.1002/ardp.201400381 - PubMed
-
- Mor S, Khatri M (2023) Convenient synthesis of benzothiazinoisoindol-11-ones and benzoindenothiazin-11-ones, and antimicrobial testing thereof. Mol Divers 27:1223–1241. 10.1007/s11030-022-10483-9 - PubMed
-
- El-Ghwas DE, Yehia H (2022) Antibacterial efficiency of natural products against multiple-drug-resistant clinical isolates. Egypt Pharm J 21:432–439. 10.4103/epj.epj_48_22
-
- Vashistha A, Sharma N, Nanaji Y, Kumar D, Singh G, Barnwal RP et al (2023) Quorum sensing inhibitors as therapeutics: bacterial biofilm inhibition. Bioorg Chem 136:106551. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106551 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

