MCell4 with BioNetGen: A Monte Carlo simulator of rule-based reaction-diffusion systems with Python interface
- PMID: 38656994
- PMCID: PMC11073787
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011800
MCell4 with BioNetGen: A Monte Carlo simulator of rule-based reaction-diffusion systems with Python interface
Abstract
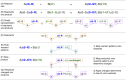
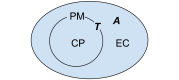
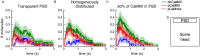
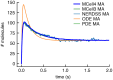
Biochemical signaling pathways in living cells are often highly organized into spatially segregated volumes, membranes, scaffolds, subcellular compartments, and organelles comprising small numbers of interacting molecules. At this level of granularity stochastic behavior dominates, well-mixed continuum approximations based on concentrations break down and a particle-based approach is more accurate and more efficient. We describe and validate a new version of the open-source MCell simulation program (MCell4), which supports generalized 3D Monte Carlo modeling of diffusion and chemical reaction of discrete molecules and macromolecular complexes in solution, on surfaces representing membranes, and combinations thereof. The main improvements in MCell4 compared to the previous versions, MCell3 and MCell3-R, include a Python interface and native BioNetGen reaction language (BNGL) support. MCell4's Python interface opens up completely new possibilities for interfacing with external simulators to allow creation of sophisticated event-driven multiscale/multiphysics simulations. The native BNGL support, implemented through a new open-source library libBNG (also introduced in this paper), provides the capability to run a given BNGL model spatially resolved in MCell4 and, with appropriate simplifying assumptions, also in the BioNetGen simulation environment, greatly accelerating and simplifying model validation and comparison.
Copyright: © 2024 Husar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
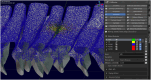
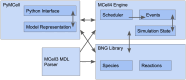
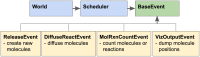

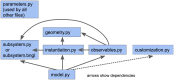












Similar articles
-
FAST MONTE CARLO SIMULATION METHODS FOR BIOLOGICAL REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS IN SOLUTION AND ON SURFACES.SIAM J Sci Comput. 2008 Oct 13;30(6):3126. doi: 10.1137/070692017. SIAM J Sci Comput. 2008. PMID: 20151023 Free PMC article.
-
MCell-R: A Particle-Resolution Network-Free Spatial Modeling Framework.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1945:203-229. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9102-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30945248 Free PMC article.
-
Rule-based modeling of biochemical systems with BioNetGen.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;500:113-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-525-1_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19399430
-
GPUPeP: Parallel Enzymatic Numerical P System simulator with a Python-based interface.Biosystems. 2020 Oct;196:104186. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2020.104186. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Biosystems. 2020. PMID: 32535178 Review.
-
Rule-based modeling of signal transduction: a primer.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;880:139-218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-833-7_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23361986 Review.
Cited by
-
A spatial model of autophosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) predicts that the lifetime of phospho-CaMKII after induction of synaptic plasticity is greatly prolonged by CaM-trapping.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 20:2024.02.02.578696. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.02.578696. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2025 Apr 04;17:1547948. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2025.1547948. PMID: 38352446 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Mitochondrial morphology governs ATP production rate.J Gen Physiol. 2023 Sep 4;155(9):e202213263. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202213263. Epub 2023 Aug 24. J Gen Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37615622 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic cleft geometry modulates NMDAR opening probability by tuning neurotransmitter residence time.Biophys J. 2025 Apr 1;124(7):1058-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2025.01.019. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 39876560 Free PMC article.
-
A spatial model of autophosphorylation of CaMKII predicts that the lifetime of phospho-CaMKII after induction of synaptic plasticity is greatly prolonged by CaM-trapping.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2025 Apr 4;17:1547948. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2025.1547948. eCollection 2025. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40255983 Free PMC article.
-
Data Hazards as An Ethical Toolkit for Neuroscience.Neuroethics. 2025;18(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s12152-024-09580-3. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Neuroethics. 2025. PMID: 39980970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stiles JR, Bartol TM. 4. In: Schutter E, editor. Monte Carlo Methods for Simulating Realistic Synaptic Microphysiology Using MCell. CRC Press; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

