Diagnostic Anatomic Imaging for Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Maximizing Strengths and Mitigating Weaknesses
- PMID: 38657156
- PMCID: PMC11245376
- DOI: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001615
Diagnostic Anatomic Imaging for Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Maximizing Strengths and Mitigating Weaknesses
Abstract
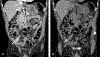
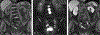
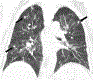
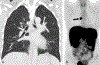
Neuroendocrine neoplasms are a heterogeneous group of gastrointestinal and lung tumors. Their diverse clinical manifestations, variable locations, and heterogeneity present notable diagnostic challenges. This article delves into the imaging modalities vital for their detection and characterization. Computed tomography is essential for initial assessment and staging. At the same time, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is particularly adept for liver, pancreatic, osseous, and rectal imaging, offering superior soft tissue contrast. The article also highlights the limitations of these imaging techniques, such as MRI's inability to effectively evaluate the cortical bone and the questioned cost-effectiveness of computed tomography and MRI for detecting specific gastric lesions. By emphasizing the strengths and weaknesses of these imaging techniques, the review offers insights into optimizing their utilization for improved diagnosis, staging, and therapeutic management of neuroendocrine neoplasms.
Copyright © 2024 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
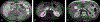
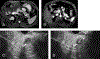
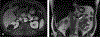
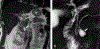
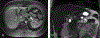
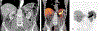
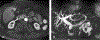
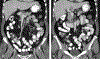
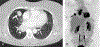
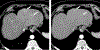
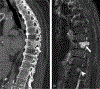
Similar articles
-
Imaging neuroendocrine tumors: Characterizing the spectrum of radiographic findings.Surg Oncol. 2021 Jun;37:101529. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101529. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33549952 Review.
-
Imaging of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 24;18(17):8895. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18178895. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Added Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging to Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Comparison With 68Ga-DOTANOC Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography.Pancreas. 2016 Mar;45(3):345-54. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000461. Pancreas. 2016. PMID: 26418904
-
State-of-the-Art Hybrid Imaging of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2024 Jul-Aug 01;48(4):510-520. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001594. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2024. PMID: 38518197 Review.
-
Simultaneous 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/MRI in patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: initial results.Invest Radiol. 2013 May;48(5):273-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182871a7f. Invest Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23493121
References
-
- Haider M, Al-Toubah T, El-Haddad G, et al. Molecular imaging and radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumors. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020;27:16–21. - PubMed
-
- Rizen EN, Phan AT. Neuroendocrine tumors: a relevant clinical update. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Rindi G, Mete O, Uccella S, et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr Pathol. 2022;33: 115–154. - PubMed
-
- Neuroendocrine tumors - statistics. Cancer.net Available at: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/neuroendocrine-tumors/statistics (2012). Accessed January 3, 2023.
-
- Bodei L, Sundin A, Kidd M, et al. The status of neuroendocrine tumor imaging: from darkness to light? Neuroendocrinology. 2015;101:1–17. - PubMed

