The Danish investigation on iodine intake and thyroid disease (DanThyr): history and implications
- PMID: 38657651
- PMCID: PMC11227094
- DOI: 10.1530/ETJ-23-0230
The Danish investigation on iodine intake and thyroid disease (DanThyr): history and implications
Abstract
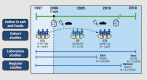
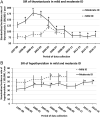
Due to mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency in Denmark, health authorities initiated a voluntary iodine fortification (IF) program in 1998, which became mandatory in 2000. In line with recommendations from the World Health Organization, the Danish investigation on iodine intake and thyroid disease (DanThyr) was established to monitor the effect on thyroid health and disease. The program involved different study designs and followed two Danish sub-populations in the years before IF and up till 20 years after. Results showed that the IF was successfully implemented and increased the level of iodine intake from mild-moderate iodine deficiency to low adequacy. The level of thyroglobulin and thyroid volume decreased following IF, and there was an indication of fewer thyroid nodules. The incidence of hyperthyroidism increased transiently following IF but subsequently decreased below the pre-fortification level. Conversely, thyroid-stimulating hormone levels and the prevalence of thyroid autoimmunity increased along with an increase in the incidence of hypothyroidism. These trends were mirrored in the trends in treatments for thyroid disease. Most differences in thyroid health and disease between regions with different iodine intake levels before IF attenuated. This review illustrates the importance of a monitoring program to detect both beneficial and adverse effects and exemplifies how a monitoring program can be conducted when a nationwide health promotion program - as IF - is initiated.
Keywords: epidemiology; iodine; public health; thyroid disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that may be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the study reported.
Figures

References
-
- World Health O, International Council for Control of Iodine Deficiency D & United Nations Children's F. Indicators for Assessing Iodine Deficiency Disorders and Their Control through Salt Iodization: Geneva: World Health Organization; 1994.
-
- Munkner T. Urinary excretion of 127 iodine in the Danish population. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 196924134.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

