Risk factors for severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a Chinese cohort of very preterm infants
- PMID: 38657990
- PMCID: PMC11147577
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.4.20230741
Risk factors for severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a Chinese cohort of very preterm infants
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the risk factors for severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in a cohort of very preterm infants (VPIs) in China, as BPD is common among VPIs and associated with a high mortality rate.
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective study, medical records from infants with BPD born at gestation age (GA) of <32 weeks with birth weight (BW) of <1,500 grams (g) in 7 regions of China were included. The cohort was stratified into different BPD severity groups based on their fraction of inspired oxygen requirement at a modified GA of 36 weeks or post discharge. Risk factors were identified using logistic regression analysis.
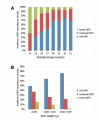
Results: A significant inverse correlation was revealed between BPD severity and both GA and BW (p<0.001). Independent risk factors for severe BPD (sBPD) were identified as invasive mechanical ventilation (≥7d), multiple blood transfusion (≥3), nosocomial infection (NI), hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (hsPDA), delayed initiation of enteral nutrition, and longer time to achieve total caloric intake of 110 kcal/kg. Conversely, administration of antenatal steroids was associated with reduced risk of sBPD.
Conclusion: Our study not only reaffirmed the established risk factors of low GA and BW for sBPD in VPIs, but also identified additional, potentially modifiable risk factors. Further research is warranted to explore whether intervention in these modifiable factors might reduce the risk of sBPD.Clinical Trial Reg. No.: ChiCTR1900023418.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; nutrition; risk factor; very preterm infants; very-low-birth-weight infants.
Copyright: © Saudi Medical Journal.
Figures
References
-
- Jobe AH, Bancalari E.. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: 1723-1729. - PubMed
-
- Shah PS, Lui K, Sjörs G, Mirea L, Reichman B, Adams M, et al. . Neonatal outcomes of very low birth weight and very preterm neonates: an international comparison. J Pediatr 2016; 177: 144-152.e6. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Preterm birth. [Updated 2018; accessed 2018. Aug 14]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preterm-birth
-
- Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Stark AR, et al. . Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007; 196: 147.e1-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

