This is a preprint.
Bridging the Gap: Multi-Omics Profiling of Brain Tissue in Alzheimer's Disease and Older Controls in Multi-Ethnic Populations
- PMID: 38659743
- PMCID: PMC11042309
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.16.589592
Bridging the Gap: Multi-Omics Profiling of Brain Tissue in Alzheimer's Disease and Older Controls in Multi-Ethnic Populations
Update in
-
Bridging the gap: Multi-omics profiling of brain tissue in Alzheimer's disease and older controls in multi-ethnic populations.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7174-7192. doi: 10.1002/alz.14208. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39215503 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Multi-omics studies in Alzheimer's disease (AD) revealed many potential disease pathways and therapeutic targets. Despite their promise of precision medicine, these studies lacked African Americans (AA) and Latin Americans (LA), who are disproportionately affected by AD.
Methods: To bridge this gap, Accelerating Medicines Partnership in AD (AMP-AD) expanded brain multi-omics profiling to multi-ethnic donors.
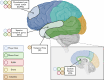
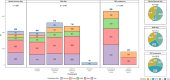
Results: We generated multi-omics data and curated and harmonized phenotypic data from AA (n=306), LA (n=326), or AA and LA (n=4) brain donors plus Non-Hispanic White (n=252) and other (n=20) ethnic groups, to establish a foundational dataset enriched for AA and LA participants. This study describes the data available to the research community, including transcriptome from three brain regions, whole genome sequence, and proteome measures.
Discussion: Inclusion of traditionally underrepresented groups in multi-omics studies is essential to discover the full spectrum of precision medicine targets that will be pertinent to all populations affected with AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; data descriptor; multi-omics; precision medicine; proteome; transcriptome; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bridging the gap: Multi-omics profiling of brain tissue in Alzheimer's disease and older controls in multi-ethnic populations.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7174-7192. doi: 10.1002/alz.14208. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39215503 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with florbetapir for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012216.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164603 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Barriers and Facilitators to Signing Up for a Mobile-Responsive Registry to Recruit Healthy Volunteers and Members of Underrepresented Communities for Alzheimer's Disease Prevention Studies.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023;10(4):865-874. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2023.67. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37874109 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease genetic risk: Top African American risk allele frequencies and genetic architecture among Mexican-, African-, and non-Hispanic White Americans.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025 Jun 19;11(2):e70124. doi: 10.1002/trc2.70124. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025. PMID: 40539127 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with flutemetamol for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012884. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012884. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164602 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG062181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG074879/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG062418/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
