This is a preprint.
PIP4K2C inhibition reverses autophagic flux impairment induced by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 38659941
- PMCID: PMC11042293
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.15.589676
PIP4K2C inhibition reverses autophagic flux impairment induced by SARS-CoV-2
Update in
-
PIP4K2C inhibition reverses autophagic flux impairment induced by SARS-CoV-2.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 10;16(1):6397. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61759-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40640184 Free PMC article.
Abstract
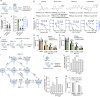
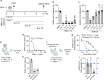
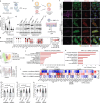
In search for broad-spectrum antivirals, we discovered a small molecule inhibitor, RMC-113, that potently suppresses the replication of multiple RNA viruses including SARS-CoV-2 in human lung organoids. We demonstrated selective dual inhibition of the lipid kinases PIP4K2C and PIKfyve by RMC-113 and target engagement by its clickable analog. Advanced lipidomics revealed alteration of SARS-CoV-2-induced phosphoinositide signature by RMC-113 and linked its antiviral effect with functional PIP4K2C and PIKfyve inhibition. We discovered PIP4K2C's roles in SARS-CoV-2 entry, RNA replication, and assembly/egress, validating it as a druggable antiviral target. Integrating proteomics, single-cell transcriptomics, and functional assays revealed that PIP4K2C binds SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 6 and regulates virus-induced impairment of autophagic flux. Reversing this autophagic flux impairment is a mechanism of antiviral action of RMC-113. These findings reveal virus-induced autophagy regulation via PIP4K2C, an understudied kinase, and propose dual inhibition of PIP4K2C and PIKfyve as a candidate strategy to combat emerging viruses.
Figures



References
-
- Weaver S.C., Ferro C., Barrera R., Boshell J. & Navarro J.-C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis. Annual Reviews in Entomology 49, 141–174 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
