Shared Activities as a Protective Factor Against Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia and Caregiver Stress
- PMID: 38660116
- PMCID: PMC11037273
- DOI: 10.1093/geroni/igae034
Shared Activities as a Protective Factor Against Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia and Caregiver Stress
Abstract
Background and objectives: Most persons with dementia experience behavioral and psychological symptoms (BPSD). While there is evidence that structured activity programs can be beneficial for persons with dementia and their caregivers, it is not well understood how joint engagement in shared activities affects BPSD and caregiver stress. The purpose of this study was to examine the moderating effect of doing a shared activity on the BPSD and caregiver stress.
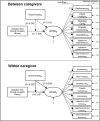
Research design and methods: This study used an intensive longitudinal observational design in which caregivers completed baseline and once-a-day diary surveys for 21 days. Caregivers were asked whether they did a pleasant noncare activity with their relative, the presence of 8 BPSD, and their stress level. A moderation model in a structural equation model examined the relationship between these variables.
Results: Our sample consisted of 453 caregivers (87.4% female, 51.4% non-Hispanic White, mean age 53 years [standard deviation {SD}: 14]) and person living with dementia whose mean age was 79 years (SD: 9). On days when the caregivers engaged in a shared activity together with person living with dementia, there was a significant decrease in the BPSD (estimate -0.038, standard error [SE] = 0.016, 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.069, -0.007, p value = 0.018). The effects of engaging in a shared activity decreased the impact of caregiver stress by 0.052 (estimate -0.052, SE = 0.018, 95% CI: -0.087, -0.017, p value = 0.004). At the between-person level, no differences were found in BPSD across caregivers who engaged or did not engage in shared activities.
Discussion and implications: The results of our study indicate that doing a shared activity is associated with reduced BPSD among persons with dementia and may buffer the impact of caregiver stress on BPSD. Shared activities should be considered a key intervention component for dementia caregivers.
Keywords: Activities; Caregiving; Dementia; Quantitative research methods; Stress.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Baharudin, A. D., Din, N. C., Subramaniam, P., & Razali, R. (2019). The associations between behavioral-psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) and coping strategy, burden of care and personality style among low-income caregivers of patients with dementia. BMC Public Health, 19(4), 447. 10.1186/s12889-019-6868-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Butler, M., Gaugler, J., Talley, K., Abdi, H., Desai, P., Duval, S., Forte, M., Nelson, V., Ng, W., & Ouellette, J. (2020). Care interventions for people living with dementia and their caregivers. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 231 (Prepared by the Minnesota Evidence-based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-2015-00008-I; AHRQ Publication No. 20-EHC023). 10.23970/AHRQEPCCER231 - DOI