Anti- Malassezia globosa (MYA-4889, ATCC) activity of Thai propolis from the stingless bee Geniotrigona thoracica
- PMID: 38660263
- PMCID: PMC11041017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29421
Anti- Malassezia globosa (MYA-4889, ATCC) activity of Thai propolis from the stingless bee Geniotrigona thoracica
Abstract
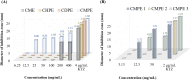
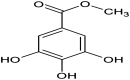
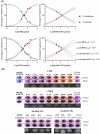
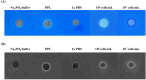
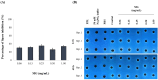
Malassezia globosa, a lipophilic pathogen, is known to be involved in various chronic skin diseases. Unfortunately, the available treatments have unwanted side effects and microbial drug resistance is evolving. As the antimicrobial activity of propolis is outstanding, this study aimed to examine the potential of propolis from the stingless bee Geniotrigona thoracica against the yeast. Anti-M. globosa growth activity was ascertained in agar well diffusion and broth microdilution assays and the inhibitory concentration value at 50 % (IC50) was determined. Since the yeast cannot synthesize its own fatty acids, extracellular lipase is important for its survival. Here, anti-M. globosa extracellular lipase activity was additionally investigated by colorimetric and agar-based methods. Compared to the crude hexane and crude dichloromethane extracts, the crude methanol partitioned extract (CMPE) exhibited the best anti-M. globosa growth activity with an IC50 of 1.22 mg/mL. After CMPE was further enriched by silica gel column chromatography, fraction CMPE1 (IC50 of 0.98 mM or 184.93 μg/mL) presented the highest activity and was later identified as methyl gallate (MG) by nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. Subsequently, MG was successfully synthesized and shown to have a similar activity, and a minimal fungicidal concentration of 43.44 mM or 8.00 mg/mL. However, lipase assay analysis suggested that extracellular lipase might not be the main target mechanism of MG. This is the first report of MG as a new anti-Malassezia compound. It could be a good candidate for further developing alternative therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Antimicrobial drug; Bee product; Lipase; Natural product; Skin disease.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Propolis from the Stingless Bee Trigona incisa from East Kalimantan, Indonesia, Induces In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Cancer Cell lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(15):6581-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.15.6581. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26434878
-
In Vitro Antimycotic Activity and Structural Damage against Canine Malassezia pachydermatis Strains Caused by Mexican Stingless Bee Propolis.Vet Sci. 2024 Feb 28;11(3):106. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11030106. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38535840 Free PMC article.
-
First report of fatty acids in Mimosadiplotricha bee pollen with in vitro lipase inhibitory activity.PeerJ. 2022 Jan 3;10:e12722. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12722. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35036098 Free PMC article.
-
Malassezia globosa and restricta: breakthrough understanding of the etiology and treatment of dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis through whole-genome analysis.J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2007 Dec;12(2):15-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.jidsymp.5650049. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2007. PMID: 18004291 Review.
-
Use of Stingless Bee Propolis and Geopropolis against Cancer-A Literature Review of Preclinical Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;14(11):1161. doi: 10.3390/ph14111161. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

