Is resilience a unifying concept for the biological sciences?
- PMID: 38660410
- PMCID: PMC11039332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109478
Is resilience a unifying concept for the biological sciences?
Abstract
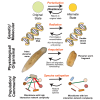
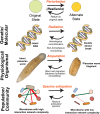
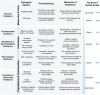
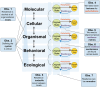
There is increasing interest in applying resilience concepts at different scales of biological organization to address major interdisciplinary challenges from cancer to climate change. It is unclear, however, whether resilience can be a unifying concept consistently applied across the breadth of the biological sciences, or whether there is limited capacity for integration. In this review, we draw on literature from molecular biology to community ecology to ascertain commonalities and shortcomings in how resilience is measured and interpreted. Resilience is studied at all levels of biological organization, although the term is often not used. There is a suite of resilience mechanisms conserved across biological scales, and there are tradeoffs that affect resilience. Resilience is conceptually useful to help diverse researchers think about how biological systems respond to perturbations, but we need a richer lexicon to describe the diversity of perturbations, and we lack widely applicable metrics of resilience.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Ecology; Evolutionary biology; Molecular biology; Systems biology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Davis J.E., Kolozsvary M.B., Pajerowska-Mukhtar K.M., Zhang B. Toward a universal theoretical framework to understand robustness and resilience: from cells to systems. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021;8 doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.579098. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

