Prevalence and Associated Factors of Sensorineural Hearing Impairment Among Patients with T2DM in Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2022: A Multi-Centered Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38660464
- PMCID: PMC11041992
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S455164
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Sensorineural Hearing Impairment Among Patients with T2DM in Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2022: A Multi-Centered Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Generally, people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in various countries experience a significant rate of sensorineural hearing impairment. Nonetheless, there is scant evidence of sensorineural hearing impairment among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Northwest Ethiopian. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the occurrence rate and contributing factors of sensorineural hearing impairment in type 2 diabetics at comprehensive and specialized referral hospitals in Northwest Ethiopia.
Methods: A facility-based cross-sectional study design was carried out from May 3, 2022, to June 14, 2022, on 846 study participants in Ethiopia, with a response rate of 99.65%. The research subjects were chosen by simple random sampling techniques. Data was gathered by using audiometric measurements and structured interview-administered questionnaires and then entered into EPI data version 4.6. Finally, it was exported to STATA 14 for analysis. Binary logistic regression, chi-square test, and odds ratio were done to verify the assumptions and degree of association. Ultimately, factors exhibiting a p-value < 0.05 with a 95% CI were regarded as significant predictors of hearing impairment.
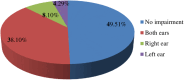
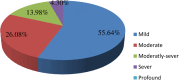
Results: The magnitude of sensorineural hearing impairment in this investigation was 50.49% (95% CI: 45.67%, 55.26%). Factors significantly associated with sensorineural hearing impairment were age (AOR=1.10, 95% CI: 1.07, 1.14), hyperlipidemia (AOR=2.86, 95% CI: 1.05, 7.82), duration of diabetes (AOR=2.26, 95% CI: 1.26, 4.06), hypertension (AOR=1.94, 95% CI: 1.02, 3.69) and regular physical exercise (AOR=0.25, 95% CI: 0.09, 0.68).
Conclusions and recommendations: In this study, relatively high rates of sensorineural hearing impairment were observed. Stakeholders should establish routine hearing screening, and participants will advise to incorporate regular physical exercise into their routines.
Keywords: Ethiopia; audiometer; diabetes; hearing loss; impairment.
© 2024 Esubalew et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and factors associated with Diabetes retinopathy among type 2 diabetic patients at Northwest Amhara Comprehensive Specialized Hospitals, Northwest Ethiopia 2021.BMC Ophthalmol. 2023 Jan 5;23(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02746-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36604682 Free PMC article.
-
Visual impairment and its predictors among people living with type 2 diabetes mellitus at Dessie town hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia: institution-based cross-sectional study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb 3;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02292-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35114950 Free PMC article.
-
HIV is still a major public health problem among pregnant women attending ANC in Referral Hospitals of the Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia: a cross sectional study.BMC Womens Health. 2022 Nov 24;22(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12905-022-02059-4. BMC Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 36434557 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Cognitive Impairment Among Stroke Survivors at Comprehensive Specialized Hospitals in Northwest Ethiopia: Multi-Centered Cross-Sectional Study.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2023 Apr 27;19:265-277. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S405357. eCollection 2023. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 37138791 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced-stage presentation of cancer at the time of diagnosis and its associated factors among adult cancer patients at Northwest Amhara comprehensive specialized hospitals, Northwest Ethiopia 2022.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 12;24(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11835-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38216966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khakurel G, Mahato NB. Evaluation of hearing loss by pure tone audiometry in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nepalese Med J. 2020;3(1):286–289. doi:10.3126/nmj.v3i1.28221 - DOI
-
- Pemmaiah KD, Srinivas DR. Hearing loss in Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Collab Res Inter Med Public Health. 2011;3(10):725–731.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources