Computed tomography-based radiomics diagnostic approach for differential diagnosis between early- and late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38660647
- PMCID: PMC11037050
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1256
Computed tomography-based radiomics diagnostic approach for differential diagnosis between early- and late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: One of the primary reasons for the dismal survival rates in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is that most patients are usually diagnosed at late stages. There is an urgent unmet clinical need to identify and develop diagnostic methods that could precisely detect PDAC at its earliest stages.
Aim: To evaluate the potential value of radiomics analysis in the differentiation of early-stage PDAC from late-stage PDAC.
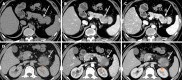
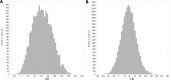
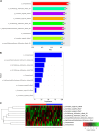
Methods: A total of 71 patients with pathologically proved PDAC based on surgical resection who underwent contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) within 30 d prior to surgery were included in the study. Tumor staging was performed in accordance with the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. Radiomics features were extracted from the region of interest (ROI) for each patient using Analysis Kit software. The most important and predictive radiomics features were selected using Mann-Whitney U test, univariate logistic regression analysis, and minimum redundancy maximum relevance (MRMR) method. Random forest (RF) method was used to construct the radiomics model, and 10-times leave group out cross-validation (LGOCV) method was used to validate the robustness and reproducibility of the model.
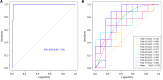
Results: A total of 792 radiomics features (396 from late arterial phase and 396 from portal venous phase) were extracted from the ROI for each patient using Analysis Kit software. Nine most important and predictive features were selected using Mann-Whitney U test, univariate logistic regression analysis, and MRMR method. RF method was used to construct the radiomics model with the nine most predictive radiomics features, which showed a high discriminative ability with 97.7% accuracy, 97.6% sensitivity, 97.8% specificity, 98.4% positive predictive value, and 96.8% negative predictive value. The radiomics model was proved to be robust and reproducible using 10-times LGOCV method with an average area under the curve of 0.75 by the average performance of the 10 newly built models.
Conclusion: The radiomics model based on CT could serve as a promising non-invasive method in differential diagnosis between early and late stage PDAC.
Keywords: American Joint Committee on Cancer staging; Computed tomography; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Radiomics.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Miller FH, Lopes Vendrami C, Hammond NA, Mittal PK, Nikolaidis P, Jawahar A. Pancreatic Cancer and Its Mimics. Radiographics. 2023;43:e230054. - PubMed
-
- Guler GD, Ning Y, Ku CJ, Phillips T, McCarthy E, Ellison CK, Bergamaschi A, Collin F, Lloyd P, Scott A, Antoine M, Wang W, Chau K, Ashworth A, Quake SR, Levy S. Detection of early stage pancreatic cancer using 5-hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in circulating cell free DNA. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5270. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagai M, Nakamura K, Terai T, Kohara Y, Yasuda S, Matsuo Y, Doi S, Sakata T, Sho M. Significance of multiple tumor markers measurements in conversion surgery for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2023;23:721–728. - PubMed
-
- Kim SS, Lee S, Lee HS, Bang S, Han K, Park MS. Retrospective Evaluation of Treatment Response in Patients with Nonmetastatic Pancreatic Cancer Using CT and CA 19-9. Radiology. 2022;303:548–556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

