[Data integration centers-from a concept in the Medical Informatics Initiative to its local implementation in the Network of University Medicine]
- PMID: 38662020
- PMCID: PMC11166806
- DOI: 10.1007/s00103-024-03879-5
[Data integration centers-from a concept in the Medical Informatics Initiative to its local implementation in the Network of University Medicine]
Abstract
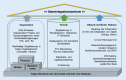
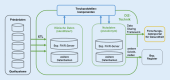
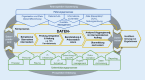
As part of the Medical Informatics Initiative (MII), data integration centers (DICs) have been established at 38 university and 3 non-university locations in Germany since 2018. At DICs, research and healthcare data are collected. The DICs represent an important pillar in research and healthcare. They establish the technical, organizational, and (ethical) data protection requirements to enable cross-site research with the available routine clinical data.This article presents the three main pillars of DICs: ethical-legal framework, organization, and technology. The organization of DICs and their organizational embedding and interaction are presented, as well as the technical infrastructure. The services that a DIC provides for its own location and for external researchers are explained, and the role of the DIC as an internal and external interface for strengthening cooperation and collaboration is outlined.Legal conformity, organization, and technology form the basis for the processes and structures of a DIC and are decisive for how it is integrated into the healthcare and research landscape of a location, but also for how it can react to national and European requirements and act and function as an interface to the outside world. In this context and with regard to national developments (e.g., introduction of the electronic patient file-ePA), but also international and European initiatives (e.g., European Health Data Space-EHDS), the DIC will play a central role in the future.
Im Rahmen der Medizininformatik-Initiative (MII) sind seit 2018 an 38 universitären sowie 3 nichtuniversitären Standorten in Deutschland Datenintegrationszentren (DIZ) entstanden. Hier werden Forschungs- und Versorgungsdaten zusammengetragen. Die Datenintegrationszentren (DIZ) stellen mittlerweile eine wichtige Säule in der Forschung und Versorgung dar. Sie schaffen die technischen, organisatorischen und (ethisch-)datenschutzrechtlichen Voraussetzungen, um mit den vorhandenen klinischen Routinedaten auch standortübergreifende Forschung zu ermöglichen.In diesem Beitrag werden die 3 Hauptsäulen der DIZ vorgestellt: ethisch-rechtlicher Rahmen, Organisation und Technik. Die Organisation von DIZ sowie deren organisatorische Einbettung und Interaktion werden vorgestellt ebenso wie die technische Infrastruktur. Die Services, die ein DIZ für den eigenen Standort und für externe Forschende erbringt, werden erklärt und die Rolle des DIZ als Schnittstelle nach innen und außen zur Stärkung der Kooperation und Kollaboration dargelegt.Rechtskonformität, Organisation und Technik bilden die Grundlagen für Prozesse und Strukturen eines DIZ und sind einerseits entscheidend dafür, wie es in die Versorgungs- und Forschungslandschaft eines Standortes integriert ist, andererseits aber auch dafür, wie es auf nationale und europäische Anforderungen reagieren und als Schnittstelle nach außen agieren und fungieren kann. In diesem Kontext und im Hinblick auf die nationalen Entwicklungen (z. B. Einführung der elektronischen Patientenakte – ePA), aber auch die internationalen und europäischen Initiativen (z. B. Europäischer Gesundheitsdatenraum – EHDS) werden die DIZ zukünftig eine zentrale Rolle spielen.
Keywords: Data integration; Digitalization; Health research data services; Realworld Data.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The Medical Informatics Initiative at a glance-establishing a health research data infrastructure in Germany].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024 Jun;67(6):616-628. doi: 10.1007/s00103-024-03887-5. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024. PMID: 38837053 Free PMC article. German.
-
The Concept of a Versatile Computing Tool Chain for Utilizing the Core Data Set of the Medical Informatics Initiative in the INTERPOLAR Project.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024 Aug 30;317:59-66. doi: 10.3233/SHTI240838. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024. PMID: 39234707
-
[Interoperability Working Group: core dataset and information systems for data integration and data exchange in the Medical Informatics Initiative].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024 Jun;67(6):656-667. doi: 10.1007/s00103-024-03888-4. Epub 2024 May 16. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024. PMID: 38753022 Free PMC article. German.
-
[Digital health progress hubs-data integration beyond university hospitals].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024 Jun;67(6):701-709. doi: 10.1007/s00103-024-03883-9. Epub 2024 May 16. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024. PMID: 38753021 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Facilitating biomedical researchers' interrogation of electronic health record data: Ideas from outside of biomedical informatics.J Biomed Inform. 2016 Apr;60:376-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Biomed Inform. 2016. PMID: 26972838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EyeMatics: An Ophthalmology Use Case Within the German Medical Informatics Initiative.JMIR Med Inform. 2024 Dec 5;12:e60851. doi: 10.2196/60851. JMIR Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 39637381 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in detecting and predicting adverse drug events via distributed analysis of electronic health record data from German university hospitals.PLOS Digit Health. 2025 Jun 26;4(6):e0000892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000892. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLOS Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40569944 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Interoperable Electronic Health Record (EHR) Data for Distributed Analyses in Clinical Research: Technical Implementation Report of the HELP Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Jul 30;13:e68171. doi: 10.2196/68171. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40737605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wikipedia (2023) Big Data. https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_Data. Zugegriffen: 20. Nov. 2023
-
- Schreiweis B, Ammon D, Sedlmayr M, Albashiti F, Wendt T. Das Datenintegrationszentrum – Ausgangspunkt für die datengetriebene medizinische Forschung und Versorgung. Mdi – Forum Medizin Dokumentation Medizin-informatik. 2019;21(4):106–110.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

