The foundation for investigating factor XI as a target for inhibition in human cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 38662114
- PMCID: PMC11645312
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-024-02985-0
The foundation for investigating factor XI as a target for inhibition in human cardiovascular disease
Abstract
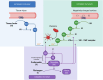
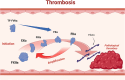
Anticoagulant therapy is a mainstay in the management of patients with cardiovascular disease and related conditions characterized by a heightened risk for thrombosis. Acute coronary syndrome, chronic coronary syndrome, ischemic stroke, and atrial fibrillation are the most common. In addition to their proclivity for thrombosis, each of these four conditions is also characterized by local and systemic inflammation, endothelial/endocardial injury and dysfunction, oxidative stress, impaired tissue-level reparative capabilities, and immune dysregulation that plays a critical role in linking molecular events, environmental triggers, and phenotypic expressions. Knowing that cardiovascular disease and thrombosis are complex and dynamic, can the scientific community identify a common pathway or specific point of interface susceptible to pharmacological inhibition or alteration that is likely to be safe and effective? The contact factors of coagulation may represent the proverbial "sweet spot" and are worthy of investigation. The following review provides a summary of the fundamental biochemistry of factor XI, its biological activity in thrombosis, inflammation, and angiogenesis, new targeting drugs, and a pragmatic approach to managing hemostatic requirements in clinical trials and possibly day-to-day patient care in the future.
Keywords: Factor XI; Hemostasis; Monoclonal antibodies; Small molecule inhibitors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factor XI and factor XII as targets for new anticoagulants.Thromb Res. 2016 May;141 Suppl 2:S40-5. doi: 10.1016/S0049-3848(16)30363-2. Thromb Res. 2016. PMID: 27207423 Review.
-
2017 Scientific Sessions Sol Sherry Distinguished Lecture in Thrombosis: Factor XI as a Target for New Anticoagulants.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Feb;38(2):304-310. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309664. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29269514 Review.
-
Factor XI and XII as antithrombotic targets.Curr Opin Hematol. 2011 Sep;18(5):349-55. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283497e61. Curr Opin Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21730835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors IX, XI, and XII: potential therapeutic targets for anticoagulant therapy in atherothrombosis.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Dec 30;20(4):245-253. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm.2019.04.56. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 31912715 Review.
-
Factor XI inhibitors for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A new therapeutic approach on the horizon?Blood Rev. 2023 Nov;62:101119. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2023.101119. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Blood Rev. 2023. PMID: 37580207 Review.
Cited by
-
Venous thromboembolism prevention and treatment with factor XI/XIa inhibitors: current status and future perspectives.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03132-z. Online ahead of print. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40627281 Review.
-
Safety of factor XI inhibitors compared to factor X inhibitors in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jul 3. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03142-x. Online ahead of print. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40610712
References
-
- Gailani D, Broze GJ Jr (1991) Factor XI activation in a revised model of blood coagulation. Science 253(5022):909–912. 10.1126/science.1652157 - PubMed
-
- Bouma BN, Griffin JH (1977) Human blood coagulation factor XI. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XII. J Biol Chem 252(18):6432–6437 - PubMed
-
- McMullen BA, Fujikawa K, Davie EW (1991) Location of the disulfide bonds in human coagulation factor XI: the presence of tandem apple domains. Biochemistry 30(8):2056–2060. 10.1021/bi00222a008 - PubMed
-
- Walsh PN, Sinha D, Koshy A, Seaman FS, Bradford H (1986) Functional characterization of platelet-bound factor XIa: retention of factor XIa activity on the platelet surface. Blood 68(1):225–230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

