Discovery of antiplasmodial pyridine carboxamides and thiocarboxamides
- PMID: 38663046
- PMCID: PMC11068522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2024.100536
Discovery of antiplasmodial pyridine carboxamides and thiocarboxamides
Abstract
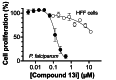
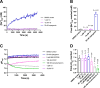
Malaria continues to be a significant burden, particularly in Africa, which accounts for 95% of malaria deaths worldwide. Despite advances in malaria treatments, malaria eradication is hampered by insecticide and antimalarial drug resistance. Consequently, the need to discover new antimalarial lead compounds remains urgent. To help address this need, we evaluated the antiplasmodial activity of twenty-two amides and thioamides with pyridine cores and their non-pyridine analogues. Twelve of these compounds showed in vitro anti-proliferative activity against the intraerythrocytic stage of Plasmodium falciparum, the most virulent species of Plasmodium infecting humans. Thiopicolinamide 13i was found to possess submicromolar activity (IC50 = 142 nM) and was >88-fold less active against a human cell line. The compound was equally effective against chloroquine-sensitive and -resistant parasites and did not inhibit β-hematin formation, pH regulation or PfATP4. Compound 13i may therefore possess a novel mechanism of action.
Keywords: Amides; Antiplasmodial; Malaria; P. falciparum; Pyridine; Thioamides.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ashton T.D., Dans M.G., Favuzza P., Ngo A., Lehane A.M., Zhang X., Qiu D., Chandra Maity B., De N., Schindler K.A., Yeo T., Park H., Uhlemann A., Churchyard A., Baum J., Fidock D., Jarman K., Lowes K., Baud D., Brand S., Jackson P., Cowman A., Sleebs B. Optimization of 2,3-dihydroquinazolinone-3-carboxamides as antimalarials targeting PfATP4. J. Med. Chem. 2023;66(5):3540–3565. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c02092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christensen S.B. Drugs and drug leads based on natural products for treatment and prophylaxis of malaria. Evidence-Based Validation of Herbal Medicine. 2015:307–319. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800874-4.00014-3. Elsevier. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

