Anatomical and volumetric description of the guiana dolphin (Sotalia guianensis) brain from an ultra-high-field magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 38664257
- PMCID: PMC11485192
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-024-02789-1
Anatomical and volumetric description of the guiana dolphin (Sotalia guianensis) brain from an ultra-high-field magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
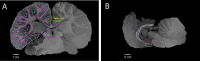
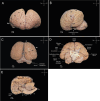
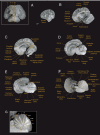
The Guiana dolphin (Sotalia guianensis) is a common species along Central and South American coastal waters. Although much effort has been made to understand its behavioral ecology and evolution, very little is known about its brain. The use of ultra-high field MRI in anatomical descriptions of cetacean brains is a very promising approach that is still uncommon. In this study, we present for the first time a full anatomical description of the Guiana dolphin's brain based on high-resolution ultra-high-field magnetic resonance imaging, providing an exceptional level of brain anatomical details, and enriching our understanding of the species. Brain structures were labeled and volumetric measurements were delineated for many distinguishable structures, including the gray matter and white matter of the cerebral cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, superior and inferior colliculi, thalamus, corpus callosum, ventricles, brainstem and cerebellum. Additionally, we provide the surface anatomy of the Guiana dolphin brain, including the labeling of main sulci and gyri as well as the calculation of its gyrification index. These neuroanatomical data, absent from the literature to date, will help disentangle the history behind cetacean brain evolution and consequently, mammalian evolution, representing a significant new source for future comparative studies.
Keywords: Brain evolution; Comparative neuroanatomy; Dolphin brain; MRI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Stitcher: A Surface Reconstruction Tool for Highly Gyrified Brains.Neuroinformatics. 2024 Oct;22(4):539-554. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09678-2. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Neuroinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39387991 Free PMC article.
-
Guiana dolphins (Sotalia guianensis) as marine ecosystem sentinels: ecotoxicology and emerging diseases.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;228:1-29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-01619-1_1. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24162090 Review.
-
Volumetric neuroimaging of the atlantic white-sided dolphin (Lagenorhynchus acutus) brain from in situ magnetic resonance images.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2008 Mar;291(3):263-82. doi: 10.1002/ar.20654. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2008. PMID: 18286607
-
Captive-born intergeneric hybrid of a Guiana and bottlenose dolphin: Sotalia guianensis x Tursiops truncatus.Zoo Biol. 2010 Sep-Oct;29(5):647-57. doi: 10.1002/zoo.20299. Zoo Biol. 2010. PMID: 20033990
-
Neuroanatomic and magnetic resonance imaging references for normal development of cerebral sulci of laboratory primate, cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2012 Mar;52(1):16-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2011.00352.x. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2012. PMID: 22348780 Review.
Cited by
-
Stitcher: A Surface Reconstruction Tool for Highly Gyrified Brains.Neuroinformatics. 2024 Oct;22(4):539-554. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09678-2. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Neuroinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39387991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvy L (1971) Endocrine glands and hormonal secretion in cetaceans. Investig Cetacea (berne) 3:229–300
-
- Avelino-de-Souza K (2023) A multiparametric comparative analysis of structure in cetacean brains PhD thesis Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas. Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro
-
- Baron G, Stephan H, Frahm HD (1996) Comparative neurobiology in Chiroptera. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel; Boston
-
- Becegato EZ, Andrade JP, Guimaraes JP, Vergara-Parente JE, Miglino MA, SILVA, F. M. (2015) Reproductive morphology of female Guiana dolphins (Sotalia guianensis). An Acad Bras Ciênc 87:1727–1736. 10.1590/0001-3765201520140432 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

