Human and camel cystic echinococcosis - a polyclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for its serodiagnosis with molecular identification
- PMID: 38664356
- PMCID: PMC11315795
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-024-10375-3
Human and camel cystic echinococcosis - a polyclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for its serodiagnosis with molecular identification
Abstract
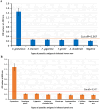
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is an emergent neglected disease affecting human and animals in Egypt with a wide distribution and incidence. This study aimed to evaluate the use of a polyclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA in the detection of Echinococcus granulosus antigen in human and camel sera. Hydatid cyst protoscoleces antigen (PsAg) was isolated from hydatid cysts collected from naturally infected camel livers and lungs. PsAg was used for immunization of rabbits to raise IgG polyclonal antibodies (IgG PsAb). IgG PsAb were then precipitated, purified using Protein-A Sepharose gel and labeled with horseradish peroxidase enzyme. We assayed the purity of the IgG PsAb, and the two prepared E. granulosus antigens CPsAg from camel cysts and HPsAg from human cysts by Sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The resulted protein bands of the prepared CPsAg appeared at different molecular weights: 180, 90, 68, 54, 42 and 22 kDa while, HPsAg shared with it in 4 common bands at 68, 54, 42, and 22 kDa. The purified IgG PsAb had been resolved at two bands at 52 kDa and at 32 kDa. Sandwich ELISA were performed for the detection of circulating E. granulosus antigens in sera of human (n = 183) and camels (n = 190). The purified IgG PsAb showed strong reactivity against E. granulosus infected human and camel samples and no cross reactivity neither with free-healthy negative sera nor with others parasitic diseases (Schistosomiasis, Fascioliasis, Toxoplasmosis, Ancylostomiasis for human samples and Fascioliasis, ticks' infestation, Eimeriosis, Cryptosporidiosis, Nasal myiasis, Toxoplasmosis for camel samples). The sensitivity of the assay was 98.25% (56/57) and 96.9% (31/32) against human and camel samples, respectively. Specificity was 100% in both human and camel samples. Sandwich ELISA detected CE in 33.3% (24/72) and 55.6% (50/90) random human and camel samples, respectively. Indirect ELISA, using CPsAg, was used for detection of antibodies in positive human and camels' sera and detected 96.5% (55/57) and 93.8% (30/32) of human and camel samples, respectively. In our study, Genomic DNA was extracted from protoscoleces fluid of human liver hydatid cysts to identify the Echinococcus sp. isolate based on NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (NAD1) gene by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and the isolate (GenBank: OP785689.1) were identified as E. granulosus sensu lato genotype. In conclusion, Sandwich ELISA technique was found to be a potent and sensitive assay for detection of hydatid antigen in both human and camel samples.
Keywords: Echinococcus granulosus; Indirect ELISA; PCR; Protein-A sepharose gel affinity chromatography; SDS-page; Sandwich ELISA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Abd El Hafez SM, Anwar AM, Ibrahim AM, Mahmoud MB, Hassan HM (2010) Preparation of fluoresce isothiocyanate conjugated IgG (FITC) anti-camel and anti-buffalo. Nat Sci J 8:342–347
-
- Aboelhadid SM, El-Dakhly KM, Yanai T, Fukushi H, Hassanin KM (2013) Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in Egyptian donkeys. Vet Parasitol 193:292–296 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

