Reduced intensity versus myeloablative conditioning for MDS: long-term results of an EBMT phase III study (RICMAC)
- PMID: 38664589
- PMCID: PMC11296945
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-024-02282-7
Reduced intensity versus myeloablative conditioning for MDS: long-term results of an EBMT phase III study (RICMAC)
Abstract
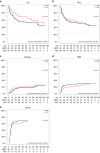
Short-term outcome of myeloablative (MAC) and reduced intensity (RIC) conditioning in the prospective randomized international EBMT RICMAC study in patients with myelodyplastic syndrome (MDS) was comparable but longer follow up is lacking. Patients with MDS aged 18-65 years were randomized to receive MAC (N = 64) with busulfan/cyclophosphamide or RIC (n = 65) with busulfan/fludarabine followed by stem cell transplantation -(HCT) from HLA matched or mismatched donor. After a median follow-up of 6.2 (0.4-12.5) years, 10-year OS and RFS were 54.0% and 43.9% for RIC and 44.4% and 44.2% for MAC (p = 0.15 and p = 0.78), respectively. Since the first report, 6 patients died on NRM, 4 after RIC, and 2 after MAC. Similarly, 8 patients relapsed (4 in each arm), increasing the number of relapsed patients to 28. The second HCT was performed in 18 pts, 8 in the MAC, and 10 in the RIC arm. In a multivariate analysis, ECOG status and chemotherapy prior to HCT were independent risk factors for OS and RFS, ECOG and low cytogenetic risk for NRM and chemotherapy prior to HCT for RI. Patients with low cytogenetic risk had better OS [p = 0.002], RFS [p = 0.02], and NRM (p = 0.015) after RIC as compared to MAC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The study was funded in part by Pierre Fabre. NK received an honorarium from Novartis, Neovii, Riemser, and BMS. PD consultancy for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Beigene, BMS, Gilead, Miltenyi, Novartis, Riemser; speakers’ bureau for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Gilead, Novartis, Riemser, Roche; research support from Riemser (all to institution). WB received Honoraries and Travel Grants from Medac, Miltenyi, BMS, Janssen, and Novartis. MR received research funding (independent studies) from AbbVie, Novartis, Medac, and Astex. LPM received an honorarium from Pfizer, Gilead Novartis, Amgen, Jazz, and Neovii.KH received research support from Celgene/BMS, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Roche, and Sanofi and honorarium from AbbVie, EUSA Pharma, Gilead, Incyte, Novartis, Roche, Beigene, Celgene/BMS, EUSA Pharma, Incyte, Roche, Sanofi. UP received honoraria from Abbvie, Celgene/Jazz, Curis, Geron, and Janssen for consulting or advisory roles from BMS GmbH & Co KG, Celgene/Jazz, and Novartis, research funding from Amgen, BerGenBio, Celgene, Curis, Janssen, and Novartis, and travel sponsoring, accommodations, and expenses from Celgene. DPM received honoraria/consultation fees from Novartis, Jazz Pharma, and partial participation in a company-sponsored bureau (AbbVie, CTI).
Figures


References
-
- Kroger N, Iacobelli S, Franke GN, Platzbecker U, Uddin R, Hubel K, et al. Dose-reduced versus standard conditioning followed by allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a prospective randomized phase III study of the EBMT (RICMAC Trial). J Clin Oncol. 2017; JCO2016707349. 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7349. - PubMed
-
- Kroger N, Sockel K, Wolschke C, Bethge W, Schlenk RF, Wolf D et al. Comparison between 5-azacytidine treatment and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in elderly patients with advanced MDS according to donor availability (VidazaAllo Study). J Clin Oncol. 2021: JCO2002724. 10.1200/JCO.20.02724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

