The enhancement of astaxanthin production in Phaffia rhodozyma through a synergistic melatonin treatment and zinc finger transcription factor gene overexpression
- PMID: 38666259
- PMCID: PMC11043562
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1367084
The enhancement of astaxanthin production in Phaffia rhodozyma through a synergistic melatonin treatment and zinc finger transcription factor gene overexpression
Abstract
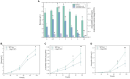
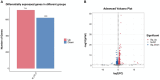
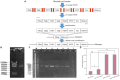
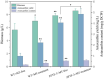
Astaxanthin has multiple physiological functions and is applied widely. The yeast Phaffia rhodozyma is an ideal source of microbial astaxanthin. However, the stress conditions beneficial for astaxanthin synthesis often inhibit cell growth, leading to low productivity of astaxanthin in this yeast. In this study, 1 mg/L melatonin (MT) could increase the biomass, astaxanthin content, and yield in P. rhodozyma by 21.9, 93.9, and 139.1%, reaching 6.9 g/L, 0.3 mg/g DCW, and 2.2 mg/L, respectively. An RNA-seq-based transcriptomic analysis showed that MT could disturb the transcriptomic profile of P. rhodozyma cell. Furthermore, differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis show that the genes induced or inhibited significantly by MT were mainly involved in astaxanthin synthesis, metabolite metabolism, substrate transportation, anti-stress, signal transduction, and transcription factor. A mechanism of MT regulating astaxanthin synthesis was proposed in this study. The mechanism is that MT entering the cell interacts with components of various signaling pathways or directly regulates their transcription levels. The altered signals are then transmitted to the transcription factors, which can regulate the expressions of a series of downstream genes as the DEGs. A zinc finger transcription factor gene (ZFTF), one of the most upregulated DEGs, induced by MT was selected to be overexpressed in P. rhodozyma. It was found that the biomass and astaxanthin synthesis of the transformant were further increased compared with those in MT-treatment condition. Combining MT-treatment and ZFTF overexpression in P. rhodozyma, the biomass, astaxanthin content, and yield were 8.6 g/L, 0.6 mg/g DCW, and 4.8 mg/L and increased by 52.1, 233.3, and 399.7% than those in the WT strain under MT-free condition. In this study, the synthesis and regulation theory of astaxanthin is deepened, and an efficient dual strategy for industrial production of microbial astaxanthin is proposed.
Keywords: Phaffia rhodozyma; RNA-seq; anti-stress; astaxanthin; melatonin; signal transduction; transcription factor engineering.
Copyright © 2024 Jia, Chen, Li, Li, Liu and Bao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salicylic acid treatment and overexpression of a novel polyamine transporter gene for astaxanthin production in Phaffia rhodozyma.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 19;11:1282315. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1282315. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37929196 Free PMC article.
-
The damage and tolerance mechanisms of Phaffia rhodozyma mutant strain MK19 grown at 28 °C.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Jan 7;20(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01479-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33413415 Free PMC article.
-
[Characterization and evaluation of an astaxanthin over-producing Phaffia rhodozyma].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2011 Jul;27(7):1065-75. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 22016991 Chinese.
-
Enhancing astaxanthin yield in Phaffia rhodozyma: current trends and potential of phytohormones.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 May;106(9-10):3531-3538. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11972-5. Epub 2022 May 17. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35579685 Review.
-
Advances and trends for astaxanthin synthesis in Phaffia rhodozyma.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 6;24(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02704-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40329361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basiony M., Ouyang L., Wang D., Yu J., Zhou L., Zhu M., et al. . (2022). Optimization of microbial cell factories for astaxanthin production: biosynthesis and regulations, engineering strategies and fermentation optimization strategies. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 7, 689–704. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.01.002, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellora N., Moliné M., David-Palma M., Coelho M. A., Hittinger C. T., Sampaio J. P., et al. . (2016). Comparative genomics provides new insights into the diversity, physiology, and sexuality of the only industrially exploited tremellomycete: Phaffia rhodozyma. BMC Genomics 17:901. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3244-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bu X., Lin J.-Y., Cheng J., Yang D., Duan C.-Q., Koffas M., et al. . (2020). Engineering endogenous ABC transporter with improving ATP supply and membrane flexibility enhances the secretion of β-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13:168. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01809-6, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

