α-Synuclein seed amplification assay detects Lewy body co-pathology in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease late in the disease course and dependent on Lewy pathology burden
- PMID: 38666355
- PMCID: PMC11180868
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13818
α-Synuclein seed amplification assay detects Lewy body co-pathology in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease late in the disease course and dependent on Lewy pathology burden
Abstract
Introduction: Amyloid beta and tau pathology are the hallmarks of sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and autosomal dominant AD (ADAD). However, Lewy body pathology (LBP) is found in ≈ 50% of AD and ADAD brains.
Methods: Using an α-synuclein seed amplification assay (SAA) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from asymptomatic (n = 26) and symptomatic (n = 27) ADAD mutation carriers, including 12 with known neuropathology, we investigated the timing of occurrence and prevalence of SAA positive reactivity in ADAD in vivo.
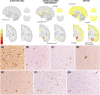
Results: No asymptomatic participant and only 11% (3/27) of the symptomatic patients tested SAA positive. Neuropathology revealed LBP in 10/12 cases, primarily affecting the amygdala or the olfactory areas. In the latter group, only the individual with diffuse LBP reaching the neocortex showed α-synuclein seeding activity in CSF in vivo.
Discussion: Results suggest that in ADAD LBP occurs later than AD pathology and often as amygdala- or olfactory-predominant LBP, for which CSF α-synuclein SAA has low sensitivity.
Highlights: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) detects misfolded α-synuclein in ≈ 10% of symptomatic autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease (ADAD) patients. CSF RT-QuIC does not detect α-synuclein seeding activity in asymptomatic mutation carriers. Lewy body pathology (LBP) in ADAD mainly occurs as olfactory only or amygdala-predominant variants. LBP develops late in the disease course in ADAD. CSF α-synuclein RT-QuIC has low sensitivity for focal, low-burden LBP.
Keywords: Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network; Lewy body pathology; alpha‐synuclein seed amplification assay; real‐time quaking‐induced conversion.
© 2024 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
JL reports speaker fees from Bayer Vital, Biogen, EISAI, Merck, Roche, TEVA, and Zambon; consulting fees from Axon Neuroscience, EISAI, and Biogen; author fees from Thieme medical publishers and W. Kohlhammer GmbH medical publishers; and is inventor in a patent “Oral Phenylbutyrate for Treatment of Human 4‐Repeat Tauopathies” (EP 23 156 122.6) filed by LMU Munich. In addition, he reports compensation for serving as chief medical officer for MODAG GmbH; is beneficiary of the phantom share program of MODAG GmbH; and is inventor in a patent “Pharmaceutical Composition and Methods of Use” (EP 22 159 408.8) filed by MODAG GmbH, all activities outside the submitted work. NCF reports consulting fees from Biogen, Eisai, Ionis, Lilly, Roche/Genentech, and Siemens all paid to UCL; he has also served on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Biogen. OH has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer, and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Amylyx, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Cerveau, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi, and Siemens. FL has research support from NIA, NIH, Biogen, Tau‐Consortium, Roche and is a consultant of Viewmind and Biogen. JCM is funded by NIH grants # P30 AG066444; P01AG003991; P01AG026276. Neither Dr. Morris nor his family owns stock or has equity interest (outside of mutual funds or other externally directed accounts) in any pharmaceutical or biotechnology company. AMG serves on SABs for Genentech and Muna Therapeutics and has received consultancy/speaker fees from Biogen. RSV reports consultancy or speaker fees from Ionis, AviadoBio, NovoNordisk, Pfizer, Neuraxpharm, and Roche diagnosis. GH has ongoing research collaborations with Roche, UCB, Abbvie; serves as a consultant for Abbvie, Alzprotect, Amylyx, Aprineua, Asceneuron, Bayer, Bial, Biogen, Biohaven, Epidarex, Ferrer, Kyowa Kirin, Lundbeck, Novartis, Retrotope, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Takeda, Teva, UCB; received honoraria for scientific presentations from Abbvie, Bayer, Bial, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kyowa Kirin, Pfizer, Roche, Teva, UCB, Zambon; holds a patent on Treatment of Synucleinopathies (US 10,918,628 B2; EP 17 787 904.6‐1109 / 3 525 788); received publication royalties from Academic Press, Kohlhammer, and Thieme. All other authors have no conflicts to report. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG079850/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- (FKZ/BMBF - German Ministry for research and Education
- Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- R01 MH120794/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- CIHR/Canada
- R01 AG062268/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- PE0000006/NextGenerationEU, Italian Ministry of University and Research, National Recovery and Resilience Plan
- U19 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Research and Development Grants for Dementia
- FKZ161L0214B,FKZ161L0214CCLINSPECT-M)/BMBF - German Ministry for research and Education
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF-2021-12374386/Ministero della Salute
- SG-20-690363-DIAN LATAM/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- HU21C0066/Korea Dementia Research Center
- Raul Carrea Institute for Neurological Research
- German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Spanish Institute of Health Carlos III
- Canadian Consortium of Neurodegeneration and Aging, Brain Canada Foundation
- U19AG032438/Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EXC2145SyNergy-ID390857198/German Research Foundation under Germany's Excellence Strategy within the framework of the Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology (SyNergy)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

