Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
- PMID: 38667030
- PMCID: PMC11047535
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13040354
Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
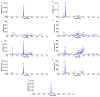
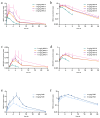
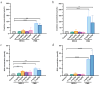
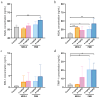
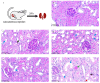
MRX-8 is a novel polymyxin for carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative infections that has been recently evaluated in Phase I clinical trials. Herein, its pharmacokinetics (PK) and nephrotoxicity in rats are reported for the first time. This study aimed at pre-clinical PK and safety assessments. An LC-MS/MS method was developed to determine concentrations of MRX-8 and its major deacylation metabolite, MRX-8039, in rat plasma. Animals were administered a single dose of MRX-8 (2, 4, 6, and 8 mg/kg) or comparator polymyxin B (PMB) (4 and 8 mg/kg) to compare the kidney injury known for the polymyxin drug class. Nephrotoxicity was evaluated using serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) biomarkers, and renal histopathology. In rats, MRX-8 displayed linear PK within the range of 2-8 mg/kg, with approximately 4% of MRX-8 converted to MRX-8039. MRX-8 induced only mild increases in serum creatinine and BUN levels, with an apparent decrease in nephrotoxicity within 24 h, in contrast to PMB, which exhibited a significant and more persistent toxicity. Additional nephrotoxicity biomarkers (plasma NGAL and urinary NGAL, KIM-1, and TIMP-1) have confirmed attenuated MRX-8 kidney injury. Histopathology has revealed significantly greater cellular/tissue toxicity for PMB as compared to MRX-8 (variances of p = 0.008 and p = 0.048 vs. saline control, respectively). Thus, MRX-8 induces a mild and reversible kidney injury in rats compared to PMB. These data support a continued evaluation of the novel polymyxin in human trials.
Keywords: MRX-8; MRX-8039; nephrotoxicity; pharmacokinetics; polymyxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wagenlehner F., Lucenteforte E., Pea F., Soriano A., Tavoschi L., Steele V.R., Henriksen A.S., Longshaw C., Manissero D., Pecini R., et al. Systematic review on estimated rates of nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity in patients treated with polymyxins. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021;27:671–686. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.12.009. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

