No Sequestration of Commonly Used Anti-Infectives in the Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Circuit-An Ex Vivo Study
- PMID: 38667049
- PMCID: PMC11047533
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13040373
No Sequestration of Commonly Used Anti-Infectives in the Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Circuit-An Ex Vivo Study
Abstract
Patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) often require therapy with anti-infective drugs. The pharmacokinetics of these drugs may be altered during ECMO treatment due to pathophysiological changes in the drug metabolism of the critically ill and/or the ECMO therapy itself. This study investigates the latter aspect for commonly used anti-infective drugs in an ex vivo setting. A fully functional ECMO device circulated an albumin-electrolyte solution through the ECMO tubes and oxygenator. The antibiotic agents cefazolin, cefuroxim, cefepime, cefiderocol, linezolid and daptomycin and the antifungal agent anidulafungin were added. Blood samples were taken over a period of four hours and drug concentrations were measured via high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection. Subsequently, the study analyzed the time course of anti-infective concentrations. The results showed no significant changes in the concentration of any tested anti-infectives throughout the study period. This ex vivo study demonstrates that the ECMO device itself has no impact on the concentration of commonly used anti-infectives. These findings suggest that ECMO therapy does not contribute to alterations in the concentrations of anti-infective medications in severely ill patients.
Keywords: ECMO; antibiotics; critical illness; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
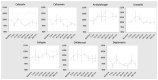
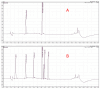
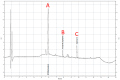

References
-
- Roberts J.A., Abdul-Aziz M.H., Lipman J., Mouton J.W., Vinks A.A., Felton T.W., Hope W.W., Farkas A., Neely M.N., Schentag J.J., et al. Individualised Antibiotic Dosing for Patients Who Are Critically Ill: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014;14:498–509. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70036-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shekar K., Roberts J.A., Smith M.T., Fung Y.L., Fraser J.F. The ECMO PK Project: An Incremental Research Approach to Advance Understanding of the Pharmacokinetic Alterations and Improve Patient Outcomes during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. BMC Anesthesiol. 2013;13:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-13-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duceppe M.A., Kanji S., Do A.T., Ruo N., Cavayas Y.A., Albert M., Robert-Halabi M., Zavalkoff S., Dupont P., Samoukovic G., et al. Pharmacokinetics of Commonly Used Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Adults During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Systematic Review. Drugs. 2021;81:1307–1329. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01557-3. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

