Real-Time Monitoring of a Nucleic Acid Amplification Reaction Using a Mass Sensor Based on a Quartz-Crystal Microbalance
- PMID: 38667148
- PMCID: PMC11048521
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14040155
Real-Time Monitoring of a Nucleic Acid Amplification Reaction Using a Mass Sensor Based on a Quartz-Crystal Microbalance
Abstract
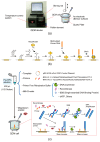
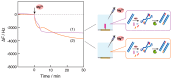
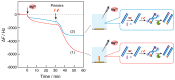
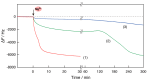
Nucleic acid amplification reactions such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which uses a DNA polymerase to amplify individual double-stranded DNA fragments, are a useful technique for visualizing the presence of specific genomes. Although the fluorescent labeling method is mainly used with DNA amplification, other detection methods should be considered for further improvements, such as miniaturization and cost reduction, of reaction-monitoring devices. In this study, the quartz-crystal microbalance (QCM) method, which can measure nanogram-order masses, was applied for the real-time detection of DNA fragments in a solution with nucleic acids. This was combined with an isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction based on the recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) method, which allowed DNA amplification at a constant temperature. When the DNA amplification reaction was initiated on a QCM sensor plate with an immobilized primer DNA strand, a significant increase in mass was observed compared to when the primer DNA was not immobilized. QCM was shown to be sufficiently sensitive for the in situ detection of amplified DNA fragments. Combining a portable QCM device and RPA offers a sensitive point-of-care method for detecting nucleic acids.
Keywords: DNA fragment detection; isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction; mass sensor; polymerase chain reaction; quartz-crystal microbalance; recombinase polymerase amplification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

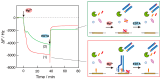

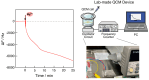
Similar articles
-
Pocketable Biosensor Based on Quartz-Crystal Microbalance and Its Application to DNA Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 27;23(1):281. doi: 10.3390/s23010281. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616883 Free PMC article.
-
Quartz crystal microbalance detection of protein amplified by nicked circling, rolling circle amplification and biocatalytic precipitation.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Mar 15;65:341-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.10.055. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25461179
-
The evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification-quartz crystal microbalance (LAMP-QCM) biosensor as a real-time measurement of HPV16 DNA.J Virol Methods. 2016 Mar;229:8-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 13. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26695714
-
Molecular Imprinting Technology in Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Feb 24;17(3):454. doi: 10.3390/s17030454. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28245588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-Time Biosensing Bacteria and Virus with Quartz Crystal Microbalance: Recent Advances, Opportunities, and Challenges.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024;54(8):2888-2899. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2023.2211164. Epub 2023 May 16. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 37191651 Review.
Cited by
-
Quartz Crystal Microbalance Analysis of Antimicrobial Protein Adsorption onto Zirconia.Materials (Basel). 2025 Aug 18;18(16):3856. doi: 10.3390/ma18163856. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40870174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hashim H.O., Al-Shuhaib M.B.S. Exploring the potential and limitations of PCR-RFLP and PCR-SSCP for SNP detection: A review. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019;6:137–144. doi: 10.29252/JABR.06.04.02. - DOI
-
- Franco-Duarte R., Černáková L., Kadam S., Kaushik K.S., Salehi B., Bevilacqua A., Corbo M.R., Antolak H., Dybka-Stępień K., Leszczewicz M., et al. Advances in chemical and biological methods to identify microorganisms-from past to present. Microorganisms. 2019;7:130. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7050130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

