Multi-Modality Imaging in Vasculitis
- PMID: 38667483
- PMCID: PMC11049623
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14080838
Multi-Modality Imaging in Vasculitis
Abstract
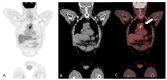
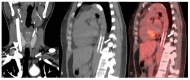
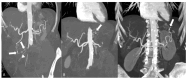
Systemic vasculitides are a rare and complex group of diseases that can affect multiple organ systems. Clinically, presentation may be vague and non-specific and as such, diagnosis and subsequent management are challenging. These entities are typically classified by the size of vessel involved, including large-vessel vasculitis (giant cell arteritis, Takayasu's arteritis, and clinically isolated aortitis), medium-vessel vasculitis (including polyarteritis nodosa and Kawasaki disease), and small-vessel vasculitis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis). There are also other systemic vasculitides that do not fit in to these categories, such as Behcet's disease, Cogan syndrome, and IgG4-related disease. Advances in medical imaging modalities have revolutionized the approach to diagnosis of these diseases. Specifically, color Doppler ultrasound, computed tomography and angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, or invasive catheterization as indicated have become fundamental in the work up of any patient with suspected systemic or localized vasculitis. This review presents the key diagnostic imaging modalities and their clinical utility in the evaluation of systemic vasculitis.
Keywords: Behçet’s disease; Cogan syndrome; Doppler ultrasound; Kawasaki disease; Takayasu’s arteritis; angiography; computed tomography; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; giant cell arteritis; granulomatosis with polyangiitis; immunoglobulin G—related disease; magnetic resonance imaging; polyarteritis nodosa; positron emission tomography; vasculitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






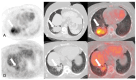
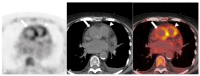


References
-
- Cid M.C., Campo E., Ercilla G., Palacin A., Vilaseca J., Villalta J., Ingelmo M. Immunohistochemical analysis of lymphoid and macrophage cell subsets and their immunologic activation markers in temporal arteritis: Influence of Corticosteroid Treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1989;32:884–893. doi: 10.1002/j.2326-5205.1989.tb00020.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maz M., Chung S.A., Abril A., Langford C.A., Gorelik M., Guyatt G., Archer A.M., Conn D.L., Full K.A., Grayson P.C., et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:1349–1365. doi: 10.1002/art.41774. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sugihara T., Hasegawa H., Uchida H.A., Yoshifuji H., Watanabe Y., Amiya E., Maejima Y., Konishi M., Murakawa Y., Ogawa N., et al. Associated factors of poor treatment outcomes in patients with giant cell arteritis: Clinical implication of large vessel lesions. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020;22:72. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02171-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

