CT Perfusion Derived rCBV < 42% Lesion Volume Is Independently Associated with Followup FLAIR Infarct Volume in Anterior Circulation Large Vessel Occlusion
- PMID: 38667490
- PMCID: PMC11049259
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14080845
CT Perfusion Derived rCBV < 42% Lesion Volume Is Independently Associated with Followup FLAIR Infarct Volume in Anterior Circulation Large Vessel Occlusion
Abstract
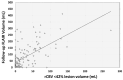
Pretreatment CT Perfusion (CTP) parameter rCBV < 42% lesion volume has recently been shown to predict 90-day mRS. In this study, we aim to assess the relationship between rCBV < 42% and a radiographic follow-up infarct volume delineated on FLAIR images. In this retrospective evaluation of our prospectively collected database, we included acute stroke patients triaged by multimodal CT imaging, including CT angiography and perfusion imaging, with confirmed anterior circulation large vessel occlusion between 9 January 2017 and 10 January 2023. Follow-up FLAIR imaging was used to determine the final infarct volume. Student t, Mann-Whitney-U, and Chi-Square tests were used to assess differences. Spearman's rank correlation and linear regression analysis were used to assess associations between rCBV < 42% and follow-up infarct volume on FLAIR. In total, 158 patients (median age: 68 years, 52.5% female) met our inclusion criteria. rCBV < 42% (ρ = 0.56, p < 0.001) significantly correlated with follow-up-FLAIR infarct volume. On multivariable linear regression analysis, rCBV < 42% lesion volume (beta = 0.60, p < 0.001), ASPECTS (beta = -0.214, p < 0.01), mTICI (beta = -0.277, p < 0.001), and diabetes (beta = 0.16, p < 0.05) were independently associated with follow-up infarct volume. The rCBV < 42% lesion volume is independently associated with FLAIR follow-up infarct volume.
Keywords: infarct volume; rCBV < 42%; relative cerebral blood volume.
Conflict of interest statement
Greg Albers, Jeremy Heit, and Vivek Yedavalli are consultants for Rapid (iSchemaView, Menlo Park, CA, USA).
Figures
References
-
- Arenillas J.F., Cortijo E., García-Bermejo P., Levy E.I., Jahan R., Liebeskind D., Goyal M., Saver J.L., Albers G.W. Relative cerebral blood volume is associated with collateral status and infarct growth in stroke patients in SWIFT PRIME. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:1839–1847. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17740293. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sohn S.W., Park H.S., Cha J.K., Kim D.H., Kang M.J., Choi J.H., Nah H.W., Huh J.T. Relative CBV ratio on perfusion-weighted MRI indicates the probability of early recanalization after IV t-PA administration for acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016;8:235–239. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011501. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imaoka Y., Shindo S., Miura M., Terasaki T., Mukasa A., Todaka T. Hypop erfusion intensity ratio and CBV index as predictive parameters to identify underlying intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in endovascular thrombectomy. J. Neuroradiol. 2023;50:424–430. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2022.10.005. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous