The Dual Lens of Endoscopy and Histology in the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38667503
- PMCID: PMC11049211
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14080858
The Dual Lens of Endoscopy and Histology in the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
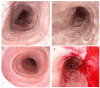
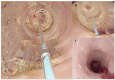
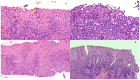
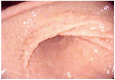
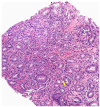
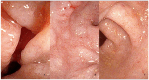
Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders (EGIDs) are a group of conditions characterized by abnormal eosinophil accumulation in the gastrointestinal tract. Among these EGIDs, Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is the most well documented, while less is known about Eosinophilic Gastritis (EoG), Eosinophilic Enteritis (EoN), and Eosinophilic Colitis (EoC). The role of endoscopy in EGIDs is pivotal, with applications in diagnosis, disease monitoring, and therapeutic intervention. In EoE, the endoscopic reference score (EREFS) has been shown to be accurate in raising diagnostic suspicion and effective in monitoring therapeutic responses. Additionally, endoscopic dilation is the first-line treatment for esophageal strictures. For EoG and EoN, while the literature is more limited, common endoscopic findings include erythema, nodules, and ulcerations. Histology remains the gold standard for diagnosing EGIDs, as it quantifies eosinophilic infiltration. In recent years, there have been significant advancements in the histological understanding of EoE, leading to the development of diagnostic scores and the identification of specific microscopic features associated with the disease. However, for EoG, EoN, and EoC, precise eosinophil count thresholds for diagnosis have not yet been established. This review aims to elucidate the role of endoscopy and histology in the diagnosis and management of the three main EGIDs and to analyze their strengths and limitations, their interconnection, and future research directions.
Keywords: EGIDs; eosinophilic GI disorders; eosinophilic colitis; eosinophilic esophagitis.
Conflict of interest statement
S.D. has served as a speaker, consultant, and advisory board member for Schering-Plough, AbbVie, Actelion, Alphawasserman, AstraZeneca, Cellerix, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Ferring, Genentech, Grunenthal, Johnson and Johnson, Millenium Takeda, MSD, Nikkiso Europe GmbH, Novo Nordisk, Nycomed, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, UCB Pharma, and Vifor. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dellon E.S., Gonsalves N., Abonia J.P., Alexander J.A., Arva N.C., Atkins D., Attwood S.E., Auth M.K., Bailey D.D., Biederman L., et al. International Consensus Recommendations for Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Nomenclature. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;20:2474–2484.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.02.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

