Physico-Chemical Properties of CdTe/Glutathione Quantum Dots Obtained by Microwave Irradiation for Use in Monoclonal Antibody and Biomarker Testing
- PMID: 38668178
- PMCID: PMC11054025
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14080684
Physico-Chemical Properties of CdTe/Glutathione Quantum Dots Obtained by Microwave Irradiation for Use in Monoclonal Antibody and Biomarker Testing
Abstract
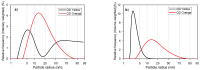
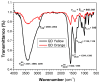
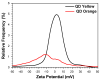
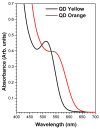
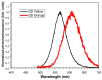
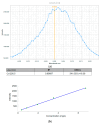
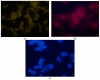
In this report, we present the results on the physicochemical characterization of cadmium telluride quantum dots (QDs) stabilized with glutathione and prepared by optimizing the synthesis conditions. An excellent control of emissions and the composition of the nanocrystal surface for its potential application in monoclonal antibody and biomarker testing was achieved. Two samples (QDYellow, QDOrange, corresponding to their emission colors) were analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS), and their hydrodynamic sizes were 6.7 nm and 19.4 nm, respectively. Optical characterization by UV-vis absorbance spectroscopy showed excitonic peaks at 517 nm and 554 nm. Photoluminescence spectroscopy indicated that the samples have a maximum intensity emission at 570 and 606 nm, respectively, within the visible range from yellow to orange. Infrared spectroscopy showed vibrational modes corresponding to the functional groups OH-C-H, C-N, C=C, C-O, C-OH, and COOH, which allows for the formation of functionalized QDs for the manufacture of biomarkers. In addition, the hydrodynamic radius, zeta potential, and approximate molecular weight were determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS), electrophoretic light scattering (ELS), and static light scattering (SLS) techniques. Size dispersion and the structure of nanoparticles was obtained by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and by X-ray diffraction. In the same way, we calculated the concentration of Cd2+ ions expressed in mg/L by using the Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES). In addition to the characterization of the nanoparticles, the labeling of murine myeloid cells was carried out with both samples of quantum dots, where it was demonstrated that quantum dots can diffuse into these cells and connect mostly with the cell nucleus.
Keywords: cadmium telluride; glutathione; microwave; murine myeloid cells; quantum dots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
One-Pot Synthesis of CdTe/ZnS Quantum Dots and their Physico-Chemical Characterization.J Fluoresc. 2024 Jul;34(4):1801-1810. doi: 10.1007/s10895-023-03406-w. Epub 2023 Aug 25. J Fluoresc. 2024. PMID: 37624469
-
Synthesis of AS1411-aptamer-conjugated CdTe quantum dots with high fluorescence strength for probe labeling tumor cells.J Fluoresc. 2014 Sep;24(5):1519-29. doi: 10.1007/s10895-014-1437-5. Epub 2014 Aug 31. J Fluoresc. 2014. PMID: 25172439
-
Synthesis of Magnetic Ions-Doped QDs Synthesized Via a Facial Aqueous Solution Method for Optical/MR Dual-Modality Imaging Applications.J Fluoresc. 2021 May;31(3):897-906. doi: 10.1007/s10895-021-02720-5. Epub 2021 Mar 27. J Fluoresc. 2021. PMID: 33772679
-
Bioinspired inimitable cadmium telluride quantum dots for bioimaging purposes.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013 Jun;13(6):3826-31. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2013.7215. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23862414
-
Rapid and green synthesis of cadmium telluride quantum dots with low toxicity based on a plant-mediated approach after microwave and ultrasonic assisted extraction: Synthesis, characterization, biological potentials and comparison study.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 May;98:535-544. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 30813055
Cited by
-
Application of Nanomaterials in Biomedical Imaging and Cancer Therapy II.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(20):1627. doi: 10.3390/nano14201627. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vassiltsova O., Jayez D., Zhao Z., Carpenter M., Petrukhina M. Synthesis of nanocomposite materials with controlled structures and optical emissions: Application of various methacrylate polymers for CdSe quantum dots encapsulation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010;10:1635–1642. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2010.2099. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbosa M.E.M., Montembault V., Cammas-Marion S., Ponchel G., Fontaine L. Synthesis and characterization of novel poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) derivatives tailored for the preparation of nanoparticles of pharmaceutical interest. Polym. Int. 2007;56:317–324. doi: 10.1002/pi.2133. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

