Determination of Bile Acids in Canine Biological Samples: Diagnostic Significance
- PMID: 38668306
- PMCID: PMC11052161
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14040178
Determination of Bile Acids in Canine Biological Samples: Diagnostic Significance
Abstract
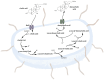
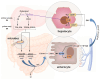
The comprehensive examination of bile acids is of paramount importance across various fields of health sciences, influencing physiology, microbiology, internal medicine, and pharmacology. While enzymatic reaction-based photometric methods remain fundamental for total BA measurements, there is a burgeoning demand for more sophisticated techniques such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for comprehensive BA profiling. This evolution reflects a need for nuanced diagnostic assessments in clinical practice. In canines, a BA assessment involves considering factors, such as food composition, transit times, and breed-specific variations. Multiple matrices, including blood, feces, urine, liver tissue, and gallbladder bile, offer insights into BA profiles, yet interpretations remain complex, particularly in fecal analysis due to sampling challenges and breed-specific differences. Despite ongoing efforts, a consensus regarding optimal matrices and diagnostic thresholds remains elusive, highlighting the need for further research. Emphasizing the scarcity of systematic animal studies and underscoring the importance of ap-propriate sampling methodologies, our review advocates for targeted investigations into BA alterations in canine pathology, promising insights into pathomechanisms, early disease detection, and therapeutic avenues.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; bile acids; canine; enterohepatic circulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Robust and Comprehensive Targeted Metabolomics Method for Quantification of 50 Different Primary, Secondary, and Sulfated Bile Acids in Multiple Biological Species (Human, Monkey, Rabbit, Dog, and Rat) and Matrices (Plasma and Urine) Using Liquid Chromatography High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS) Analysis.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Aug 4;32(8):2033-2049. doi: 10.1021/jasms.0c00435. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33826317
-
Ultra-performance chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry analysis of bile acid profiles in the enterohepatic circulation following geniposide and acetaminophen-induced liver injury.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Sep 13;1680:463417. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463417. Epub 2022 Aug 11. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 35985151
-
Quantitative bile acid profiling in healthy adult dogs and pups from serum, plasma, urine, and feces using LC-MS/MS.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jun 14;11:1380920. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1380920. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38948668 Free PMC article.
-
The bile acid profile.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 Jan 15;565:120004. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.120004. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39419312 Review.
-
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination and profiling of prohibited steroids in human biological matrices. A review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 May 15;927:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23317577 Review.
References
-
- Niu X., Xu Y., Yang Q., Tang X., Li Y., Wang Z. Analytical methods for characterization of bile acids and its application in quality control of cow-bezoar and bear bile powder. Am. J. Appl. Chem. 2014 doi: 10.11648/j.ajac.20140206.11. - DOI
-
- Sangaraju D., Katavolos P., Liang X., Chou C., Zabka T.S., Dean B., Maher J. Establishment of baseline profiles of 50 bile acids in preclinical toxicity species: A comprehensive assessment of translational differences and study design considerations for biomarker development. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022;443:116008. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

