Diphthamide deficiency promotes association of eEF2 with p53 to induce p21 expression and neural crest defects
- PMID: 38671004
- PMCID: PMC11053169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47670-1
Diphthamide deficiency promotes association of eEF2 with p53 to induce p21 expression and neural crest defects
Abstract
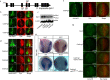
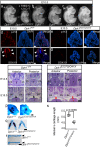
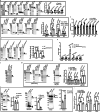
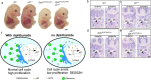
Diphthamide is a modified histidine residue unique for eukaryotic translation elongation factor 2 (eEF2), a key ribosomal protein. Loss of this evolutionarily conserved modification causes developmental defects through unknown mechanisms. In a patient with compound heterozygous mutations in Diphthamide Biosynthesis 1 (DPH1) and impaired eEF2 diphthamide modification, we observe multiple defects in neural crest (NC)-derived tissues. Knockin mice harboring the patient's mutations and Xenopus embryos with Dph1 depleted also display NC defects, which can be attributed to reduced proliferation in the neuroepithelium. DPH1 depletion facilitates dissociation of eEF2 from ribosomes and association with p53 to promote transcription of the cell cycle inhibitor p21, resulting in inhibited proliferation. Knockout of one p21 allele rescues the NC phenotypes in the knockin mice carrying the patient's mutations. These findings uncover an unexpected role for eEF2 as a transcriptional coactivator for p53 to induce p21 expression and NC defects, which is regulated by diphthamide modification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diphthamide-deficiency syndrome: a novel human developmental disorder and ribosomopathy.Eur J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov;28(11):1497-1508. doi: 10.1038/s41431-020-0668-y. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32576952 Free PMC article.
-
Diphthamide modification on eukaryotic elongation factor 2 is needed to assure fidelity of mRNA translation and mouse development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 21;109(34):13817-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206933109. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22869748 Free PMC article.
-
Elongation factor 2 diphthamide is critical for translation of two IRES-dependent protein targets, XIAP and FGF2, under oxidative stress conditions.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Feb;67:131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24140707 Free PMC article.
-
Diphthamide - a conserved modification of eEF2 with clinical relevance.Trends Mol Med. 2024 Feb;30(2):164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.11.008. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38097404 Review.
-
Novel compound heterozygous DPH1 mutations in a patient with the unique clinical features of airway obstruction and external genital abnormalities.J Hum Genet. 2018 Apr;63(4):529-532. doi: 10.1038/s10038-017-0399-2. Epub 2018 Jan 23. J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29362492 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Regulatory Interaction of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cleft Palate Induced by Retinoic Acid.Protein Pept Lett. 2025;32(1):54-61. doi: 10.2174/0109298665308502240820115618. Protein Pept Lett. 2025. PMID: 39473103
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

