Alterations in adolescent brain serotonin (5HT)1A, 5HT2A, and dopamine (D)2 receptor systems in a nonhuman primate model of early life adversity
- PMID: 38671147
- PMCID: PMC11224234
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-023-01784-0
Alterations in adolescent brain serotonin (5HT)1A, 5HT2A, and dopamine (D)2 receptor systems in a nonhuman primate model of early life adversity
Abstract
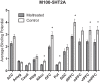
Stress affects brain serotonin (5HT) and dopamine (DA) function, and the effectiveness of 5HT and DA to regulate stress and emotional responses. However, our understanding of the long-term impact of early life adversity (ELA) on primate brain monoaminergic systems during adolescence is scarce and inconsistent. Filling this gap in the literature is critical, given that the emergence of psychopathology during adolescence has been related to deficits in these systems. Here, we use a translational nonhuman primate (NHP) model of ELA (infant maltreatment by the mother) to examine the long-term impact of ELA on adolescent 5HT1A, 5HT2A and D2 receptor systems. These receptor systems were chosen based on their involvement in stress/emotional control, as well as reward and reinforcement. Rates of maternal abuse, rejection, and infant's vocalizations were obtained during the first three postnatal months, and hair cortisol concentrations obtained at 6 months postnatal were examined as early predictors of binding potential (BP) values obtained during adolescence using positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. Maltreated animals demonstrated significantly lower 5HT1A receptor BP in prefrontal cortical areas as well as the amygdala and hippocampus, and lower 5HT2A receptor BP in striatal and prefrontal cortical areas. Maltreated animals also demonstrated significantly lower D2 BP in the amygdala. None of the behavioral and neuroendocrine measurements obtained early in life predicted any changes in BP data. Our findings suggest that early caregiving experiences regulate the development of brain 5HT and DA systems in primates, resulting in long-term effects evident during adolescence.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to American College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Peripuberty Is a Sensitive Period for Prefrontal Parvalbumin Interneuron Activity to Impact Adult Cognitive Flexibility.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(2):127-138. doi: 10.1159/000539584. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38830346 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Early (< 8 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 24;10(10):CD001146. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001146.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 21;10:CD001146. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001146.pub6. PMID: 29063585 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
The relationship between self-reported adverse experiences and depressive symptoms among middle-aged and elderly individuals: A longitudinal study based on the CHARLS database.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Apr 22;46:101001. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101001. eCollection 2025 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40386507 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids and monoaminergic system: implications for learning and memory.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 14;18:1425532. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1425532. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39206116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapman DP, Whitfield CL, Felitti VJ, Dube SR, Edwards VJ, Anda RF. Adverse childhood experiences and the risk of depressive disorders in adulthood. J Affect Disord. 2004;82:217–25. - PubMed
-
- Carr CP, Martins CMS, Stingel AM, Lemgruber VB, Juruena MF. The role of early life stress in adult psychiatric disorders: a systematic review according to childhood trauma subtypes. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2013;201:1007–20. - PubMed
-
- Cicchetti D, Toth SL. Child maltreatment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:409–38. - PubMed
-
- Danese A, Tan M. Childhood maltreatment and obesity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:544–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA038588/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- R01 DA052909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- ORIP/OD P51OD011132/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- MH078105/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

