Variable characteristics overlooked in human K-562 leukemia cell lines with a common signature
- PMID: 38671192
- PMCID: PMC11053119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60271-8
Variable characteristics overlooked in human K-562 leukemia cell lines with a common signature
Abstract
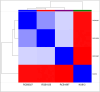
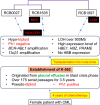
K-562 is a well-known in vitro cellular model that represents human leukemia cell lines. Although the K-562 cells have been extensively characterized, there are inconsistencies in the data across publications, showing the presence of multiple K-562 cell lines. This suggests that analyzing a single K-562 cell line is insufficient to provide reliable reference data. In this study, we compared three K-562 cell lines with different IDs (RCB0027, RCB1635, and RCB1897) to investigate the fundamental characteristics of K-562 cells. Amplifications of the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene and at 13q31 were detected in all three cell lines, whereas each genome exhibited distinctive features of sequence variants and loss of heterozygosity. This implies that each K-562 cell line can be characterized by common and unique features through a comparison of multiple K-562 cell lines. Variations in transcriptome profiles and hemoglobin synthesis were also observed among the three cell lines, indicating that they should be considered sublines that have diverged from the common ancestral K-562 despite no changes from the original cell name. This leads to unintentional differences in genotypes and/or phenotypes among cell lines that share the same name. These data show that characterizing a single K-562 cell line does not necessarily provide data that are applicable to other K-562 cells. In this context, it is essential to modify cell names in accordance with changes in characteristics during cell culture. Furthermore, our data could serve as a reference for evaluating other K-562 sublines, facilitating the discovery of new K-562 sublines with distinct characteristics. This approach results in the accumulation of K-562 sublines with diverged characteristics and expands the options available, which may help in selecting the most suitable K-562 subline for each experiment.
Keywords: Cell line authentication; Cell name; Cell subline; In vitro cellular model; Reference data.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

