Long-term health-related quality of life and mental health in patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- PMID: 38671298
- PMCID: PMC11224107
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-024-05771-3
Long-term health-related quality of life and mental health in patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Abstract
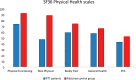
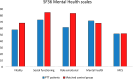
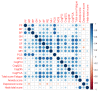
Immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) is a rare and potentially life-threatening disorder. Treatment advances have lowered morbidity rates, but past acute events can still cause long-term consequences, reducing health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and determining cognitive impairment, anxiety, and depression. We aimed to investigate these aspects and the role of caplacizumab and rituximab: 39 patients were evaluated using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), the FACIT-Fatigue, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, and the Functional Assessment in Cancer Therapy-Cognitive Function questionnaires. The median age at study inclusion was 50 years (IQR 38-60), and the median follow-up from diagnosis was 97 months (IQR 14-182); 82% of patients were female, and 36% had one or more recurrences. Caplacizumab was administered in 16 patients (41%), as well as rituximab. ITTP patients reported lower physical and mental HRQoL scores than the general population. No differences in physical or mental domains were observed between patients treated or not with caplacizumab, while those who received rituximab reported lower scores in mental health. Neurological impairment at diagnosis correlated with worse fatigue. The majority of patients (72%) reported anxiety or depression (82%). ITTP had a significant impact on the long-term cognitive function, fatigue, depression, and anxiety levels of patients, with a negative effect on their HRQoL. Our findings underscore the need to pay special attention to patients' long-term physical and mental health, regardless of the medical treatments received.
Keywords: FACT-Cog; Fatigue; HADS; HRQoL; TTP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

