Investigating the Neuroprotective and Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Bacopa monnieri: A Systematic Review Focused on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis
- PMID: 38671841
- PMCID: PMC11047749
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13040393
Investigating the Neuroprotective and Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Bacopa monnieri: A Systematic Review Focused on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis
Abstract
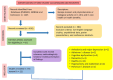
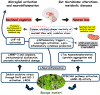
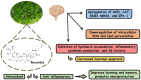
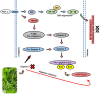
The aging of the global population has increased the prevalence of neurodegenerative conditions. Bacopa monnieri (BM), an herb with active compounds, such as bacosides A and B, betulinic acid, loliolide, asiatic acid, and quercetin, demonstrates the potential for brain health. Limited research has been conducted on the therapeutic applications of BM in neurodegenerative conditions. This systematic review aims to project BM's beneficial role in brain disorders. BM has anti-apoptotic and antioxidant actions and can repair damaged neurons, stimulate kinase activity, restore synaptic function, improve nerve transmission, and increase neuroprotection. The included twenty-two clinical trials demonstrated that BM can reduce Nuclear Factor-κB phosphorylation, improve emotional function, cognitive functions, anhedonia, hyperactivity, sleep routine, depression, attention deficit, learning problems, memory retention, impulsivity, and psychiatric problems. Moreover, BM can reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory biomarkers and oxidative stress. Here, we highlight that BM provides notable therapeutic benefits and can serve as a complementary approach for the care of patients with neurodegenerative conditions associated with brain disorders. This review adds to the growing interest in natural products and their potential therapeutic applications by improving our understanding of the mechanisms underlying cognitive function and neurodegeneration and informing the development of new therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Bacopa monnieri; cognition; inflammation; mitochondrial dysfunction; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ijaz N., Buta B., Xue Q.L., Mohess D.T., Bushan A., Tran H., Batchelor W., deFilippi C.R., Walston J.D., Bandeen-Roche K., et al. Interventions for Frailty Among Older Adults with Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022;79:482–503. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.11.029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damluji A.A., Chung S.E., Xue Q.L., Hasan R.K., Moscucci M., Forman D.E., Bandeen-Roche K., Batchelor W., Walston J.D., Resar J.R., et al. Frailty and cardiovascular outcomes in the National Health and Aging Trends Study. Eur. Heart J. 2021;42:3856–3865. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab468. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

