Specific NOX4 Inhibition Preserves Mitochondrial Function and Dampens Kidney Dysfunction Following Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury
- PMID: 38671936
- PMCID: PMC11047485
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13040489
Specific NOX4 Inhibition Preserves Mitochondrial Function and Dampens Kidney Dysfunction Following Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Kidney Injury
Abstract
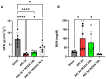
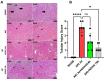
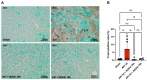
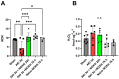
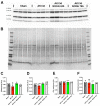
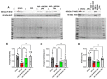
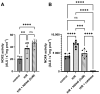
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a sudden episode of kidney failure which is frequently observed at intensive care units and related to high morbidity/mortality. Although AKI can have many different causes, ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury is the main cause of AKI. Mechanistically, NADPH oxidases (NOXs) are involved in the pathophysiology contributing to oxidative stress following IR. Previous reports have indicated that knockout of NOX4 may offer protection in cardiac and brain IR, but there is currently less knowledge about how this could be exploited therapeutically and whether this could have significant protection in IR-induced AKI. Aim: To investigate the hypothesis that a novel and specific NOX4 inhibitor (GLX7013114) may have therapeutic potential on kidney and mitochondrial function in a mouse model of IR-induced AKI. Methods: Kidneys of male C57BL/6J mice were clamped for 20 min, and the NOX4 inhibitor (GLX7013114) was administered via osmotic minipump during reperfusion. Following 3 days of reperfusion, kidney function (i.e., glomerular filtration rate, GFR) was calculated from FITC-inulin clearance and mitochondrial function was assessed by high-resolution respirometry. Renal histopathological evaluations (i.e., hematoxylin-eosin) and TUNEL staining were performed for apoptotic evaluation. Results: NOX4 inhibition during reperfusion significantly improved kidney function, as evidenced by a better-maintained GFR (p < 0.05) and lower levels of blood urea nitrogen (p < 0.05) compared to untreated IR animals. Moreover, IR caused significant tubular injuries that were attenuated by simultaneous NOX4 inhibition (p < 0.01). In addition, the level of renal apoptosis was significantly reduced in IR animals with NOX4 inhibition (p < 0.05). These favorable effects of the NOX4 inhibitor were accompanied by enhanced Nrf2 Ser40 phosphorylation and conserved mitochondrial function, as evidenced by the better-preserved activity of all mitochondrial complexes. Conclusion: Specific NOX4 inhibition, at the time of reperfusion, significantly preserves mitochondrial and kidney function. These novel findings may have clinical implications for future treatments aimed at preventing AKI and related adverse events, especially in high-risk hospitalized patients.
Keywords: NOX4; glomerular filtration rate; ischemia–reperfusion; kidney; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
Per Wikström (P.W.) has submitted European patent application no. 18171556.6, protecting the NOX4-selective compound GLX7013114. Glucox Biotech AB provided support in the form of salary for P.W. Funding from Glucox Biotech AB does not alter the company’s adherence to policy on sharing data and materials. No other potential conflicts of interest or ethical statements relevant to this article are reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dimethyl malonate preserves renal and mitochondrial functions following ischemia-reperfusion via inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase.Redox Biol. 2024 Feb;69:102984. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102984. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38061207 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Attenuates Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Ferroptosis of Tubular Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NOX4-ROS Signaling in Acute Kidney Injury.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;21(5):2313-2329. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105667. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40083709 Free PMC article.
-
NOX4 is a potential therapeutic target in septic acute kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation.Theranostics. 2023 May 8;13(9):2863-2878. doi: 10.7150/thno.81240. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37284448 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of macrophage polarization and interaction with renal tubular epithelial cells in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):28-38. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199123 Review. Chinese.
-
Organ-Specific Mitochondrial Alterations Following Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Post-Cardiac Arrest Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 5;14(4):477. doi: 10.3390/life14040477. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multivalent Immune-Protective Effects of Egg Yolk Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) Derived from Live or Inactivated Shewanella xiamenensis Against Major Aquaculture Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 21;26(14):7012. doi: 10.3390/ijms26147012. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725257 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in understanding the role of mitochondria in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s10157-025-02727-3. Online ahead of print. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40627278 Review.
-
3-methyladenine ameliorates acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative damage and apoptosis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 2;10(13):e33996. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33996. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39055838 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

