The Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Mediated F-Actin in the Acupuncture-Induced Mitigation of Inflammatory Pain in Arthritic Rats
- PMID: 38672029
- PMCID: PMC11048453
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14040380
The Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Mediated F-Actin in the Acupuncture-Induced Mitigation of Inflammatory Pain in Arthritic Rats
Abstract
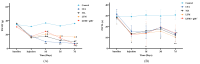
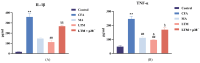
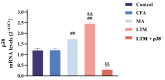
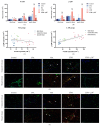
The analgesic efficacy of acupuncture has been widely recognized. However, the mechanism by which manual acupuncture-generated mechanical stimuli translate into biological signals remains unclear. This study employed a CFA-induced inflammatory pain rat model. Acupuncture intervention was then performed following standardized procedures. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) assessed inflammatory cytokines levels, while immunofluorescence and qRT-PCR screened the level of p38 and F-actin expression in the ST36 acupoint area of rats. Results indicated increased inflammatory factors, including IL-1β and TNFα, with reduced paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) and paw withdrawal thermal latency (PWTL) in CFA rats compared to unmodeled rats. After acupuncture intervention, the heightened expression level of F-actin and p38 mRNA and the phosphorylation of p38 in the acupoint area was observed alongside decreased inflammatory factors in diseased ankle joints. The application of lifting and thrusting manipulations further enhanced the effect of acupuncture, in which the molecular expression level of muscle and connective tissue increased most significantly, indicating that these two tissues play a major role in the transformation of acupuncture stimulation. Moreover, antagonizing p38 expression hindered acupuncture efficacy, supporting the hypothesis that p38 MAPK-mediated F-actin transduces mechanical signals generated by acupuncture and related manipulation into biological signals.
Keywords: acupoint area; acupuncture; inflammatory pain; p38 MAPK pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Sigma-1 Receptor/p38 MAPK Inhibition in Acupoint Catgut Embedding-Mediated Analgesic Effects in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain.Anesth Analg. 2017 Aug;125(2):662-669. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001857. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28682953
-
Chemokine CXCL1 in serum mediates the antinociceptive effect of manual acupuncture at ST36.Acupunct Med. 2021 Dec;39(6):673-680. doi: 10.1177/0964528421997435. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Acupunct Med. 2021. PMID: 33706560
-
Inhibition of chemokine CX3CL1 in spinal cord mediates the electroacupuncture-induced suppression of inflammatory pain.J Pain Res. 2019 Sep 4;12:2663-2672. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S205987. eCollection 2019. J Pain Res. 2019. PMID: 31564958 Free PMC article.
-
[Tetrahydropalmatine alleviated diabetic neuropathic pain by inhibiting activation of microglia via p38 MAPK signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 May;47(9):2533-2540. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220119.702. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35531701 Chinese.
-
Intervention of electroacupuncture on spinal p38 MAPK/ATF-2/VR-1 pathway in treating inflammatory pain induced by CFA in rats.Mol Pain. 2013 Mar 22;9:13. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-13. Mol Pain. 2013. PMID: 23517865 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Modulates Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1 on Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Pain Model.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 6;13(2):396. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020396. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002809 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

