Efficacy of Alkaline Phosphatase in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Multicentre Investigator-Initiated Double-Blind Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38672081
- PMCID: PMC11048668
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040723
Efficacy of Alkaline Phosphatase in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Multicentre Investigator-Initiated Double-Blind Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Efforts to identify therapies to treat hospitalised patients with COVID-19 are being continued. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) dephosphorylates pro-inflammatory adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into anti-inflammatory adenosine.
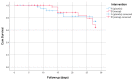
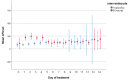
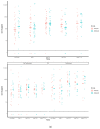
Methods: In a randomised controlled trial, we investigated the safety and efficacy of AP in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection admitted to the ICU. AP or a placebo was administered for four days following admission to the ICU. The primary outcome was the duration of mechanical ventilation. Mortality in 28 days, acute kidney injury, need for reintubation, safety, and inflammatory markers relevant to the described high cytokine release associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection were the secondary outcomes.
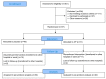
Results: Between December 2020 and March 2022, 97 patients (of the intended 132) were included, of which 51 were randomised to AP. The trial was terminated prematurely based on meeting the threshold for futility. Compared to the placebo, AP did not affect the duration of mechanical ventilation (9.0 days vs. 9.3 days, p = 1.0). No safety issues were observed. After 28 days, mortality was 9 (18%) in the AP group versus 6 (13%) in the placebo group (p = 0.531). Additionally, no statistically significant differences between the AP and the placebo were observed for the other secondary outcomes.
Conclusions: Alkaline phosphatase (AP) therapy in COVID-19 ICU patients showed no significant benefits in this trial.
Keywords: COVID-19; alkaline phosphatase; inflammatory response; mechanical ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
J.W.v.d.H. obtained a contribution for another study on alkaline phosphatase sponsored by Alloksys Lifesciences: the APhIRI-1 study (Alkaline phosphatase in renal transplantation; (ref: [21])). All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Apr;10(4):327-336. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35123660 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of intravenous plasma purified alpha-1 antitrypsin for SARS-CoV-2-induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised, controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 19;22(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05254-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33874981 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective, randomised, double blind placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia (TOC-COVID): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04447-3. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493514 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

