Apoptotic Vesicles Derived from Dental Pulp Stem Cells Promote Bone Formation through the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38672086
- PMCID: PMC11048106
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040730
Apoptotic Vesicles Derived from Dental Pulp Stem Cells Promote Bone Formation through the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
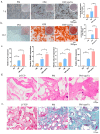
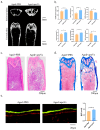
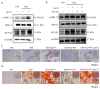
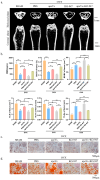
Osteoporosis is a common degenerative bone disease. The treatment of osteoporosis remains a clinical challenge in light of the increasing aging population. Human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs), a type of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), are easy to obtain and have a high proliferation ability, playing an important role in the treatment of osteoporosis. However, MSCs undergo apoptosis within a short time when used in vivo; therefore, apoptotic vesicles (apoVs) have attracted increasing attention. Currently, the osteogenic effect of DPSC-derived apoVs is unknown; therefore, this study aimed to determine the role of DPSC-derived apoVs and their potential mechanisms in bone regeneration. We found that MSCs could take up DPSC-derived apoVs, which then promoted MSC osteogenesis in vitro. Moreover, apoVs could increase the trabecular bone count and bone mineral density in the mouse osteoporosis model and could promote bone formation in rat cranial defects in vivo. Mechanistically, apoVs promoted MSC osteogenesis by activating the extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 signaling pathway. Consequently, we propose a novel therapy comprising DPSC-derived apoVs, representing a promising approach to treat bone loss and bone defects.
Keywords: ERK1/2 signaling pathway; apoptotic vesicles; bone defect; dental pulp stem cells; osteogenic differentiation; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Zhao P., Xiao L., Peng J., Peng J., Qian Y.Q., Huang C.C. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast proliferation via MAPK pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018;22:3962–3970. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H.T., Ran C.C., Liao Y.P., Zhu J.H., Wang H., Deng R., Nie M., He B.C., Deng Z.L. IGF-1 reverses the osteogenic inhibitory effect of dexamethasone on BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts via PI3K/AKT/COX-2 pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019;191:105363. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.04.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang C., Liu Y., Hu X., Shang X., Ma S., Guo H., Ma X., Cai D., Hu Z., Zhao Y., et al. Titanium dioxide nanotubes increase purinergic receptor P2Y6 expression and activate its downstream PKCα-ERK1/2 pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under osteogenic induction. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:670–682. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.11.045. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

