Molecular and Cellular Involvement in CIPN
- PMID: 38672107
- PMCID: PMC11048589
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040751
Molecular and Cellular Involvement in CIPN
Abstract
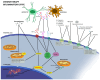
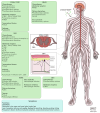
Many anti-cancer drugs, such as taxanes, platinum compounds, vinca alkaloids, and proteasome inhibitors, can cause chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). CIPN is a frequent and harmful side effect that affects the sensory, motor, and autonomic nerves, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, and reduced quality of life. The causes of CIPN are not fully known, but they involve direct nerve damage, oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA damage, microtubule dysfunction, and altered ion channel activity. CIPN is also affected by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors that modulate the risk and intensity of nerve damage. Currently, there are no effective treatments or prevention methods for CIPN, and symptom management is mostly symptomatic and palliative. Therefore, there is a high demand for better understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in CIPN, as well as the development of new biomarkers and therapeutic targets. This review gives an overview of the current knowledge and challenges in the field of CIPN, focusing on the biological and molecular mechanisms underlying this disorder.
Keywords: channels; chemotherapy; mechanisms; neuroinflammation; neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cho Y., Ruddy K.J., Lavoie Smith E.M. Evaluation of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. In: Lustberg M., Loprinzi C., editors. Diagnosis, Management and Emerging Strategies for Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy: A MASCC Book. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 53–93. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources