Mixture of Doxycycline, ML-7 and L-NAME Restores the Pro- and Antioxidant Balance during Myocardial Infarction-In Vivo Pig Model Study
- PMID: 38672140
- PMCID: PMC11047935
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040784
Mixture of Doxycycline, ML-7 and L-NAME Restores the Pro- and Antioxidant Balance during Myocardial Infarction-In Vivo Pig Model Study
Abstract
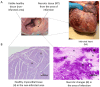
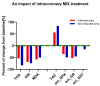
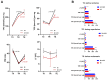
The restoration of blood flow to the ischemic myocardium inflicts ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) heart injury (IRI). The main contributors to IRI are increased oxidative stress and subsequent excessive production of ROS, increased expression of NOS and peroxinitate, activation of MMPs, and enhanced posttranslational modifications of contractile proteins, which make them more susceptible to proteolytic degradation. Since the pathophysiology of IRI is a complex issue, and thus, various therapeutic strategies are required to prevent or reduce IRI and microvascular dysfunction, in the current study we proposed an innovative multi-drug therapy using low concentrations of drugs applied intracoronary to reach microvessels in order to stabilize the pro- and antioxidant balance during a MI in an in vivo pig model. The ability of a mixture of doxycycline (1 μM), ML-7 (0.5 μM), and L-NAME (2 μM) to modulate the pro- and antioxidative balance was tested in the left ventricle tissue and blood samples. Data showed that infusion of a MIX reduced the total oxidative status (TOS), oxidative stress index (OSI), and malondialdehyde (MDA). It also increased the total antioxidant capacity, confirming its antioxidative properties. MIX administration also reduced the activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9, and then decreased the release of MLC1 and BNP-26 into plasma. This study demonstrated that intracoronary administration of low concentrations of doxycycline in combination with ML-7 and L-NAME is incredibly efficient in regulating pro- and antioxidant balance during MI.
Keywords: MI pig model; ischemia-reperfusion injury; oxidative stress; pro- and antioxidant balance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
L-NAME improves doxycycline and ML-7 cardioprotection from oxidative stress.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jan 1;23(2):298-309. doi: 10.2741/4592. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 28930548
-
Mixture of MMP-2, MLC, and NOS Inhibitors Affects NO Metabolism and Protects Heart from Cardiac I/R Injury.Cardiol Res Pract. 2020 Apr 7;2020:1561478. doi: 10.1155/2020/1561478. eCollection 2020. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32322413 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Study on Doxycycline Protective Mechanisms during Myocardial Ischemia Injury in Rats.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 13;12(3):634. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030634. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540247 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of inhibitors of MMPs and ROS-dependent modifications of contractile proteins on protection hearts subjected to oxidative stress.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(9):1345-8. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990556. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23978100 Review.
-
Protective Role of Platelets in Myocardial Infarction and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Cardiol Res Pract. 2021 May 24;2021:5545416. doi: 10.1155/2021/5545416. eCollection 2021. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34123416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac rehabilitation in porcine models: Advances in therapeutic strategies for ischemic heart disease.Zool Res. 2025 May 18;46(3):576-607. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.387. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 40343415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamm C.W., Bassand J.-P., Agewall S., Bax J., Boersma E., Bueno H., Caso P., Dudek D., Gielen S., Huber K., et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevatio. Eur. Heart J. 2011;32:2999–3054. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr236. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lønborg J., Vejlstrup N., Kelbæk H., Bøtker H.E., Kim W.Y., Mathiasen A.B., Jørgensen E., Helqvist S., Saunamäki K., Clemmensen P., et al. Exenatide reduces reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2012;33:1491–1499. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr309. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

