Correlation between rCBV Delineation Similarity and Overall Survival in a Prospective Cohort of High-Grade Gliomas Patients: The Hidden Value of Multimodal MRI?
- PMID: 38672146
- PMCID: PMC11048661
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040789
Correlation between rCBV Delineation Similarity and Overall Survival in a Prospective Cohort of High-Grade Gliomas Patients: The Hidden Value of Multimodal MRI?
Abstract
Purpose: The accuracy of target delineation in radiation treatment planning of high-grade gliomas (HGGs) is crucial to achieve high tumor control, while minimizing treatment-related toxicity. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) represents the standard imaging modality for delineation of gliomas with inherent limitations in accurately determining the microscopic extent of tumors. The purpose of this study was to assess the survival impact of multi-observer delineation variability of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) and [18F]-FET PET/CT.
Materials and methods: Thirty prospectively included patients with histologically confirmed HGGs underwent a PET/CT and mpMRI including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI: b0, b1000, ADC), contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (T1-Gado), T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (T2Flair), and perfusion-weighted imaging with computation of relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) and K2 maps. Nine radiation oncologists delineated the PET/CT and MRI sequences. Spatial similarity (Dice similarity coefficient: DSC) was calculated between the readers for each sequence. Impact of the DSC on progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was assessed using Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test.
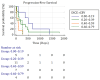
Results: The highest DSC mean values were reached for morphological sequences, ranging from 0.71 +/- 0.18 to 0.84 +/- 0.09 for T2Flair and T1Gado, respectively, while metabolic volumes defined by PET/CT achieved a mean DSC of 0.75 +/- 0.11. rCBV variability (mean DSC0.32 +/- 0.20) significantly impacted PFS (p = 0.02) and OS (p = 0.002).
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the T1-Gado and T2Flair sequences were the most reproducible sequences, followed by PET/CT. Reproducibility for functional sequences was low, but rCBV inter-reader similarity significantly impacted PFS and OS.
Keywords: MRI; PET-FET; [18F]-FET PET/CT; delineation; glioblastoma; high-grade gliomas; magnetic resonance imaging; rCBV; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the present study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radiotherapy Target Volume Definition in Newly Diagnosed High-Grade Glioma Using 18F-FET PET Imaging and Multiparametric MRI: An Inter Observer Agreement Study.Tomography. 2022 Aug 16;8(4):2030-2041. doi: 10.3390/tomography8040170. Tomography. 2022. PMID: 36006068 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy target volume definition in newly diagnosed high grade glioma using 18F-FET PET imaging and multiparametric perfusion MRI: A prospective study (IMAGG).Radiother Oncol. 2020 Sep;150:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Radiother Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32580001
-
Imaging biomarkers guided anti-angiogenic therapy for malignant gliomas.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Jul 5;20:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.001. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30069427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of IDH Mutation Status in High-grade Gliomas Using DWI and High T1-weight DSC-MRI.Acad Radiol. 2022 Mar;29 Suppl 3:S52-S62. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.02.002. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 33685792
-
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Radiotherapy Planning of Gliomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):1063. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051063. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schritz A., Aouali N., Fischer A., Dessenne C., Adams R., Berchem G., Huiart L., Schmitz S. Systematic review and network meta-analysis of the efficacy of existing treatments for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021;3:vdab052. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdab052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Effects of Radiotherapy with Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide Versus Radiotherapy Alone on Survival in Glioblastoma in a Randomised Phase III Study: 5-Year Analysis of the EORTC-NCIC Trial—PubMed. [(accessed on 31 July 2021)]; Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19269895/ - PubMed
-
- Minniti G., Amelio D., Amichetti M., Salvati M., Muni R., Bozzao A., Lanzetta G., Scarpino S., Arcella A., Enrici R.M. Patterns of failure and comparison of different target volume delineations in patients with glioblastoma treated with conformal radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Radiother. Oncol. 2010;97:377–381. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.08.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pauleit D., Floeth F., Hamacher K., Riemenschneider M.J., Reifenberger G., Müller H.-W., Zilles K., Coenen H.H., Langen K.-J. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain. 2005;128:678–687. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh399. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

